Fig. 1.
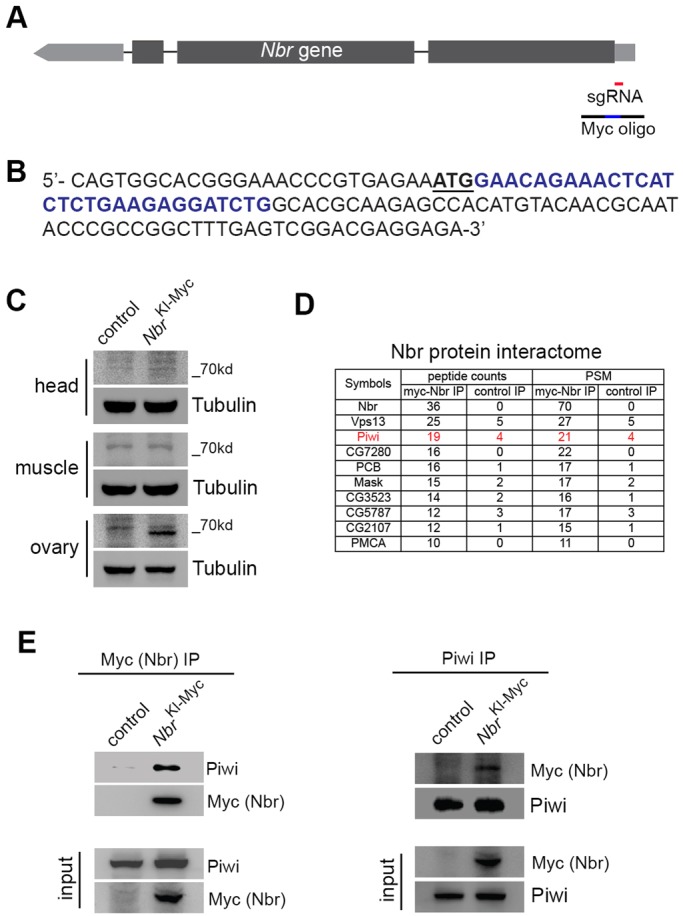
Endogenous Nbr is ovary enriched and interacts with Piwi. (A) The Drosophila Nbr locus and guiding RNAs used to make NbrKI-Myc. To produce an Nbr Myc tag knock-in allele using the CRISPR/Cas9 method, sgRNA (red) was co-injected with a DNA oligonucleotide (black line, interrupted with blue representing Myc coding sequence). (B) In NbrKI-Myc, the Nbr gene contains sequence (blue) encoding the Myc tag inserted after the Nbr ATG start codon (underlined). Resulting NbrKI-Myc flies were backcrossed to the control homogeneous background for five generations to ensure background clearance. (C) Nbr is ovary enriched. In adult flies, a protein signal corresponding to Nbr protein on the western blot could be clearly seen for the ovary, but not head or muscle. Genotypes: control (5905) and NbrKI-Myc/KI-Myc (NbrKI-Myc). (D) Endogenous protein interactome determines that Nbr interacts with Piwi. Using endogenous Nbr as bait for immunoprecipitation and mass spectroscopy analysis, Piwi (red) was captured among the top-ranked interacting proteins. Ranking was based on peptide counts. Highly stringent criteria were applied, including peptide counts greater than 10 and PSM fold change greater than 5. Proteins were from ovaries. Genotypes as in C. (E) Co-IP experiment confirming that Piwi interacts with Nbr. Proteins were from ovaries. Genotypes as in C.
