Figure 1.
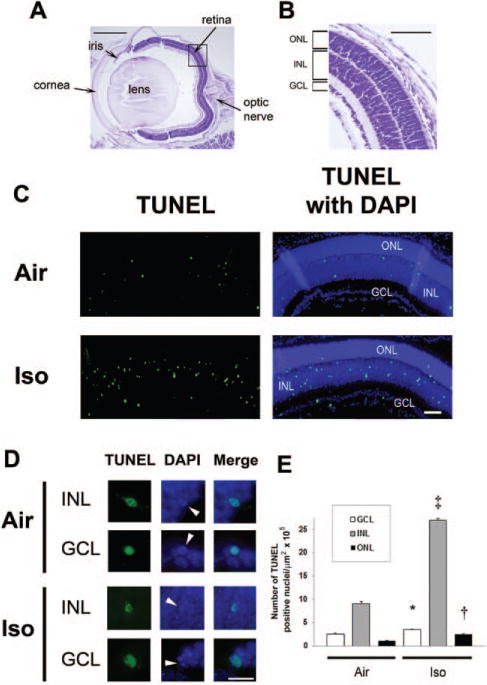
Isoflurane induces apoptosis in the developing retina. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated UTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) assays were performed on retinal sections 5 hours postexposure to isoflurane or air. A, For orientation, a cresyl violet– stained section from a mouse eye imaged at 4× is provided. The major structures including the retina and optic nerve are labeled. Scale bar, 500 μm. A magnified image of the retina within the boxed section is shown at 10× (B). The outer nuclear layer (ONL), inner nuclear layer (INL), and ganglion cell layer (GCL) are labeled. Scale bar, 250 μm. C, Representative sections of TUNEL assays with and without 4′,6-dimidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) after exposure to either air or isoflurane (Iso) at 10× are depicted. Green TUNEL-positive nuclei are visible. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, Representative images of individual TUNEL-positive nuclei within the INL and GCL magnified at 60× are demonstrated. DAPI staining of TUNEL-positive nuclei undergoing apoptosis are indicated (white arrowheads), and colocalization of fluorescence is shown in the merged images. Scale bar, 25 μm. E, Quantification of TUNEL-positive nuclei is demonstrated. Values are expressed as means + SD. N = 4–8 animals per cohort. *P = 0.022 versus air-exposed cohort, 95% confidence interval of the difference between groups (0.03–1.99). †P = 0.011 versus air-exposed cohort, 95% confidence interval (0.38–3.18). ‡P < 0.0001 versus air-exposed cohort.
