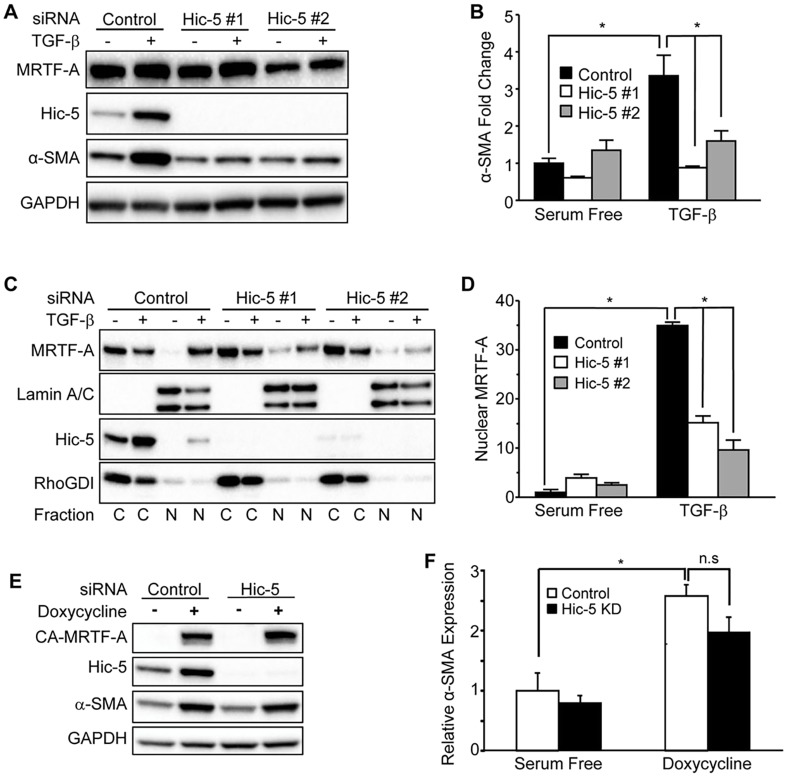
Fig. 7.
Hic-5 regulates induction of α-SMA in response to TGF-β stimulation by facilitating nuclear localization of MRTF-A. (A) NHDFs that had been transfected with non-targeting or Hic-5-targeting siRNAs were incubated (48 h) with TGF-β (10 ng/ml), lysed and analyzed by western blotting (representative, n=4). (B) Pooled data (n=4) depicting the fold change in α-SMA expression. (C) NHDFs that had been treated as described in panel A were fractioned into cytoplasmic (‘C’) or nuclear (‘N’) lysates before western blot analysis. RhoGDI and lamin A/C were used as cytoplasmic and nuclear loading controls, respectively. (D) Pooled data depicting nuclear MRTF-A levels, normalized to the levels of lamin A/C. (E) NHDFs that had been infected with a lentivirus encoding the doxycycline-inducible CA-MRTF-A construct were transfected with non-targeting or pooled Hic-5-targeting siRNAs and stimulated with doxycycline (0.5 μg/ml) for 24 h (representative, n=3). (F) Expression of CA-MRTF-A stimulated α-SMA expression to statistically similar levels, even when Hic-5 was knocked down (‘KD’). Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc analysis (*P<0.05) for panels B,D,F. Error bars are +s.e.m. n.s., not significant.