Fig. 5.
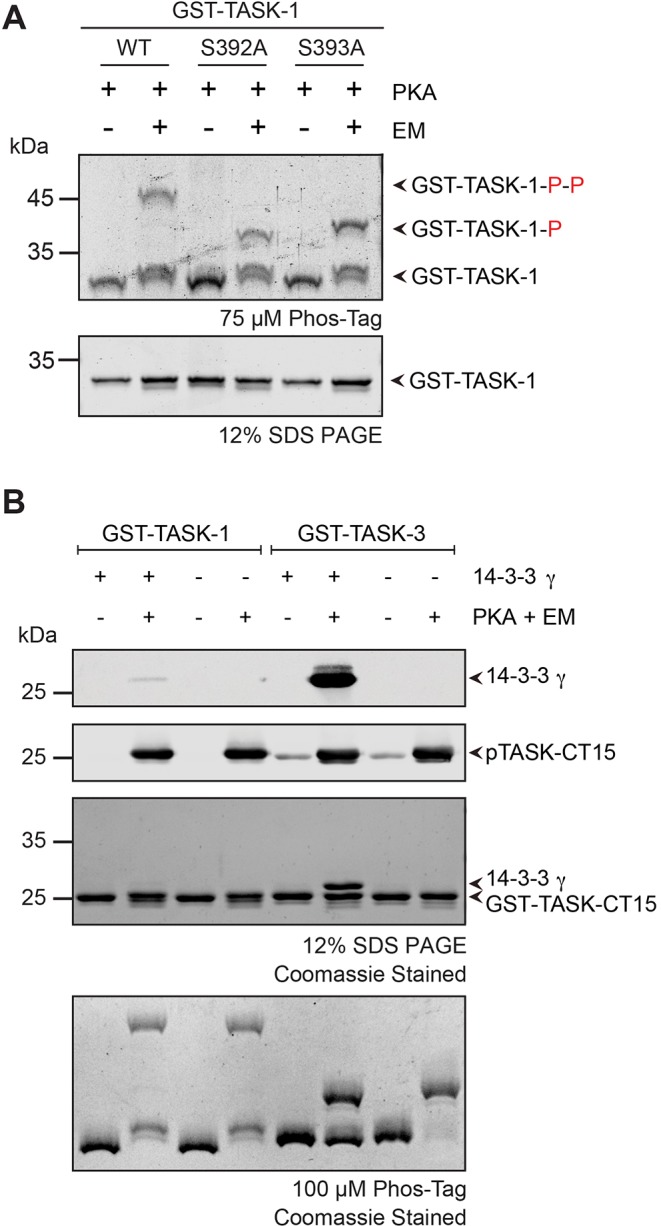
Phosphorylation of S392 in TASK-1 inhibits 14-3-3 binding. (A) In vitro phosphorylation of recombinant GST–TASK-1 wild-type, GST–TASK-1 S392A and GST–TASK-1 S393A fusion proteins with PKA catalytic subunit. Samples were resolved on an SDS-PAGE gel containing 75 µM Phostag reagent and 75 µM MnCl2. ‘P’ suffixes denote the number of phosphorylated residues. The gel is representative of three independent experiments. (B) 14-3-3 protein binding to the TASK-1 C-terminal trafficking control region is abolished by double phosphorylation. GST-TASK-1 or GST-TASK-3 C-terminal fusion proteins were in vitro phosphorylated using recombinant PKA catalytic subunit and an ATP regeneration system (energy mix; EM). Samples were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels (upper three panels) and on an SDS-PAGE gel containing 100 µM Phostag reagent and 100 µM MnCl2 (bottom). The upper two panels show western blots using antibodies against the indicated proteins, and the lower two panels show Coomassie-stained gels. TASK-CT15, the last 15 amino acids of the TASK C-terminus.
