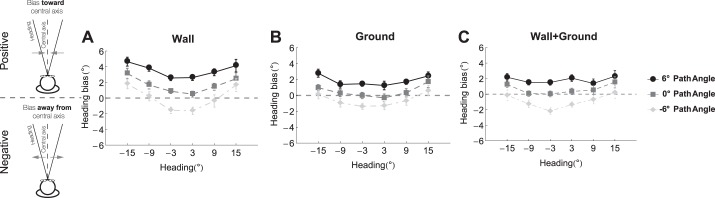
Fig. 4.
Mean bias in heading judgments in the Wall (A), Ground (B), and Wall+Ground (C) conditions from Experiment 1. Each graph shows the heading bias as a function of the heading direction. Positive bias indicates that errors in heading judgments were toward the center (central axis), negative bias indicates that errors were away from center, and the constant zero function corresponds to veridical judgments. Black, dark gray, and light gray curves in each plot correspond to performance when the object moved toward the center (δ = −6°), parallel to the observer (δ = 0°), and toward the periphery (δ = 6°), respectively. Error bars indicate ±SE. Note that unlike subsequent figures, these data are plotted without correction for the center screen bias.