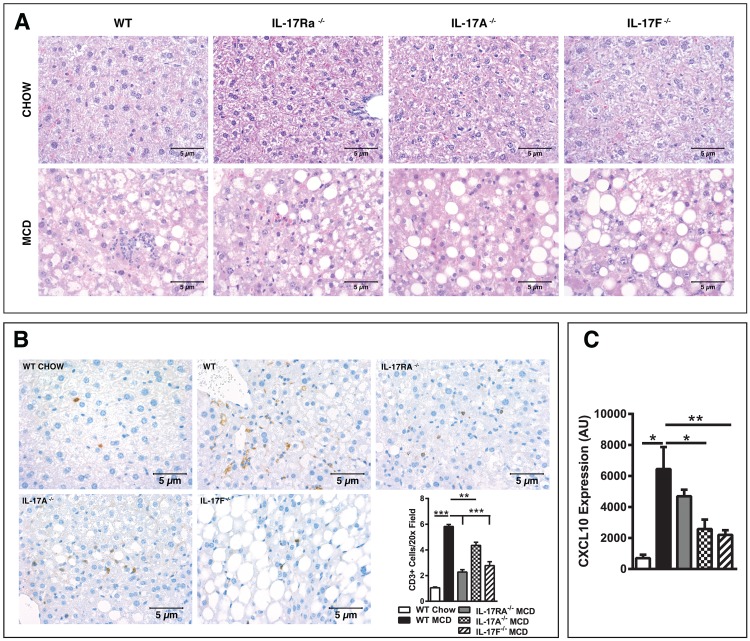
Fig 5. IL-17 Axis signaling regulates T cell infiltration to the liver.
8 week old male IL-17RA-/-, IL-17A-/-, and IL-17F-/- mice on a C57BL/6 background and WT controls (n = 4-8/condition) were placed on MCDD or chow diet for 4 weeks. (A) Representative liver histology (H&E staining; 40x). Marked difference in the level and type of steatosis and inflammation between WT and IL-17RA-/-, IL-17A-/- and IL-17F-/- mice on MCDD. No differences were noted between genotypes on a chow diet. (B) Representative immunohistochemistry staining of CD3+ T cells in the livers of WT chow, along with WT, IL-17RA-/-, IL-17A-/- and IL-17F-/- mice on MCDD and average number of CD3+ cells per 20x field. (C) Hepatic CXCL10 mRNA expression. AU = Arbitrary units, as compared to beta actin. Data represents means + SE; a representative of two separate experiments. Student t test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.