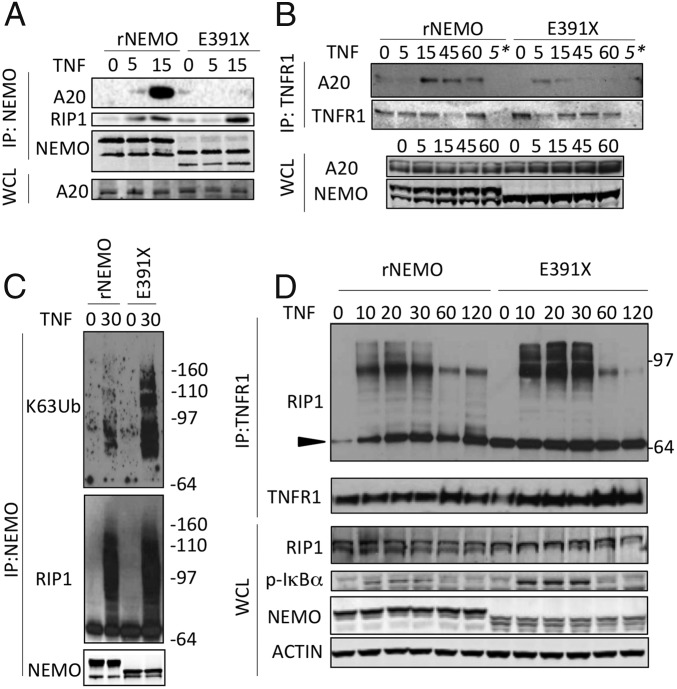
Fig. 4.
Impaired recruitment of A20 to a NEMO C terminus truncation mutant is associated with increased K63-polyubiquitinated RIP1 associated with NEMO and the TNFR. (A) Reconstituted Jurkat T Cells were stimulated with TNF for the indicated times, and NEMO was isolated by immunoprecipitation to detect NEMO/A20 association. NEMO was probed as an immunoprecipitation control. (B) Following TNF stimulation for the indicated times, the TNFR1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and the associated A20 was detected by Western blot; TNFR1 was probed as a control. The asterisk denotes IP with IgG as a control. (C) Following TNF stimulation, NEMO was immunoprecipitated and the associated RIP1 was detected in addition to specific K63 ubiquitin linkages using K63-linkage–specific antibody, NEMO was probed as an IP control. (D) Following TNF stimulation, TNF-R1 was immunoprecipitated and the associated RIP1 was detected by Western blot; unmodified RIP1 is indicated by the black triangle. RIP1, phospho-IκBα, NEMO, and actin were detected in corresponding whole-cell lysates. Experiments were performed in NEMO-deficient Jurkat cells reconstituted with either wild-type or E391X NEMO.