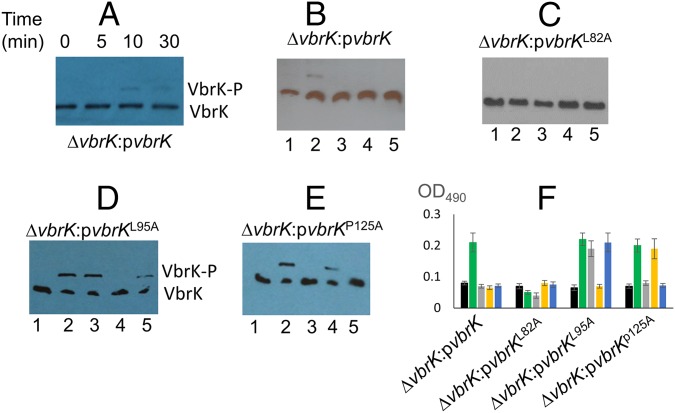
Fig. 5.
Identification of VbrK amino acid residues essential for specific recognition of different lactams. Indicated strains were cultured in M9. (A) VbrK phosphorylation was measured at different time points after carbenicillin was added to the culture. Phosphorylation of VbrK (B), VbrKL82A (C), VbrKL95A (D), and VbrKP125A (E) in V. parahaemolyticus in the presence of carbenicillin (lane 2), ε-caprolactam (lane 3), δ-valerolactam (lane 4), and 2-azacyclononanone (lane 5) or in the absence of any lactams (lane 1). (F) Indicated strains were untreated (black bar) or treated with carbenicillin (green bar), ε-caprolactam (gray bar), δ-valerolactam (yellow bar), and 2-azacyclononanone (blue bar), and OD490 was measured to indicate β-lactamase activity.