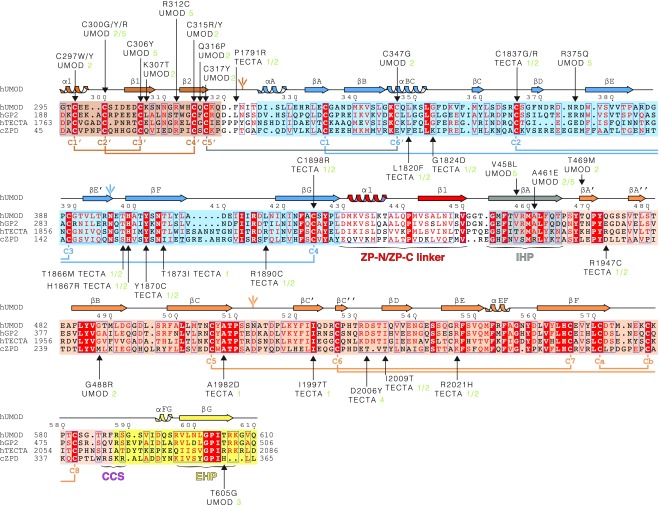
Fig. S3.
Sequence alignment of UMOD-like ZP module-containing proteins. The C-terminal extracellular regions of human GP2 and TECTA and the entire extracellular region of chicken ZPD are 55%, 37%, and 25% identical in sequence to human UMOD, respectively. Identical residues are highlighted in white and shaded in red, and conserved residues are indicated in red and marked by blue frames when clustered. Shaded boxes indicate EGF IV (brown), ZP-N (blue), and ZP-C (orange) domains, as well as IHP (gray) and external hydrophobic patch (EHP)-containing CTP (yellow). UMOD secondary structure elements, N-glycans, invariant Cys, and disulfide linkages are colored like the domains to which they belong, except for the C5′–C6′ disulfide that links EGF IV to ZP-N (gray). Arrows indicate residues affected by patient mutations, references for which are specified. Green numbers 1–4 and 5 next to pathogenic amino acid mutations indicate refs. 72–75 and the Uromodulin Kidney Disease Foundation UMOD mutation catalog (www.ukdcure.org/mutation_catalog), respectively.