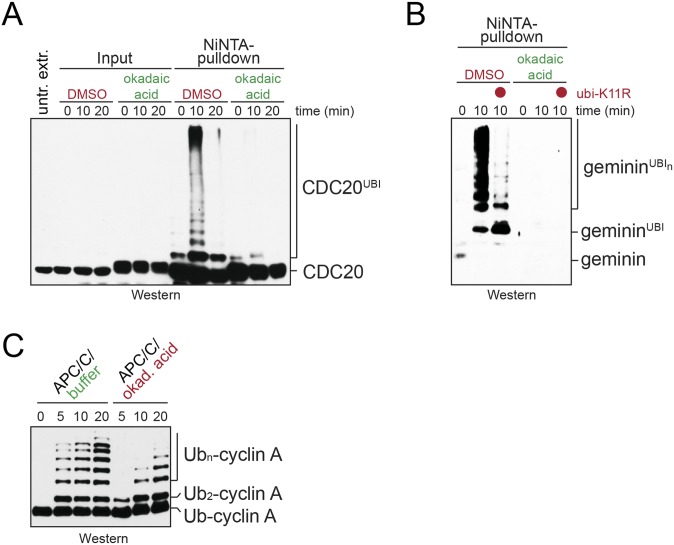
Fig. S2.
Persistent phosphorylation inhibits catalytic activation of the APC/C. (A) Phosphorylation inhibits the ability of prometaphase APC/C to catalyze the ubiquitination of endogenous Cdc20. Extracts of prometaphase HeLa cells were supplemented with His-tagged ubiquitin and treated with the phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid. After incubation at room temperature, ubiquitin conjugates were purified under denaturing conditions using NiNTA-agarose and analyzed for endogenous Cdc20 modification by Western blot analysis. (B) Phosphorylation inhibits the ability of APC/CCdc20 to catalyze K11-dependent ubiquitination of the Ube2S-substrate geminin. Extracts of prometaphase HeLa cells were supplemented with His-tagged ubiquitin or ubiquitinK11R, and ubiquitin conjugates were purified under denaturing purification as described above. Modification of endogenous geminin was detected by Western blot analysis using specific antibodies. (C) Phosphorylation inhibits activation of Ube2S by the APC/C. APC/C was purified from mitotic extracts treated with okadaic acid, as indicated, and its ability to promote Ube2S-dependent ubiquitin chain elongation toward the model substrate Ub-cyclin A was measured by Western blot analysis.