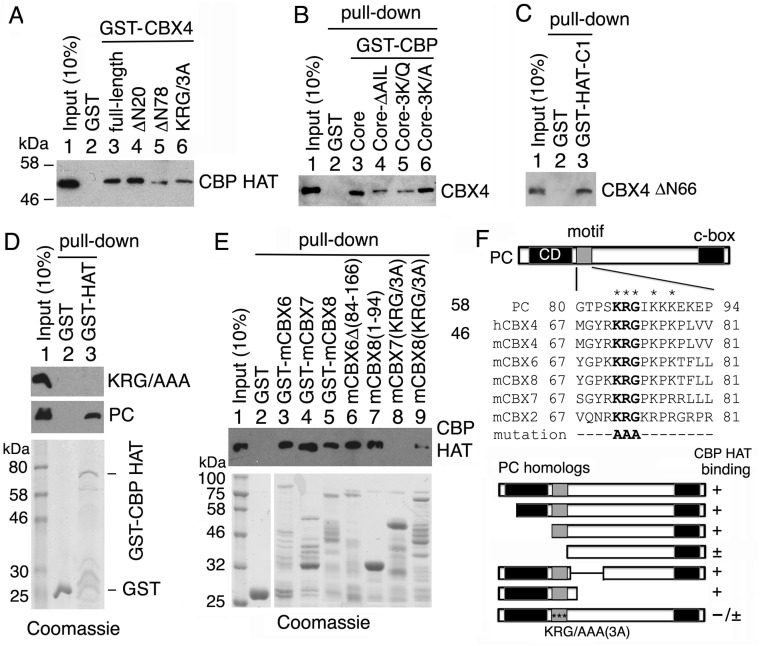
Fig. S2.
Human PC2 (CBX4) and mouse orthologs of PC bind directly to the CBP HAT domain. (A) GST-CBX4 fusion proteins (full-length, N-terminal residue deletions ΔN20 and ΔN78 and the mutation KRG73/AAA) were used to pull down purified CBP HAT domain in vitro. (B) GST-CBP core (wt, AIL-deletion, and 3K/Q or 3K/A mutations as indicated above lanes 3–6) were used to pull down purified CBX4. (C) GST-CBP-C1 (residues 2,132–2,247) was used to pull down CBX4ΔN66. All pull-down proteins (with a His-tag at the C terminus) were detected by Western blots with anti-His mAb. (D) GST and GST-CBP HAT domain were used to pull down purified PC75–228 with the KRG/AAA mutation (Top) and wt PC (Middle). (E) Pull-down of the CBP HAT domain using various forms of GST-mCBX6, GST-mCBX7, and GST-mCBX8. (D and E, Bottom) Purified GST and GST fusion proteins were stained with Coomassie blue. (F, Top) Sequence alignments of KRG motifs of PC and its mammalian CBX orthologs at the top. In addition to the conserved chromodomain (CD) at the N terminus and conserved C-terminal motif (c-box) at the C terminus, a motif with a KRG core (gray box) adjacent to the CD is highly conserved in human (h) and mouse (m) orthologs of Drosophila PC, which is absent in CBX1, CBX3, and CBX5 (orthologs of Drosophila HP-1). (F, Bottom) Results of GST pull-down of CBP HAT by mammalian orthologs of PC are summarized. Three asterisks within a gray box represent the KRG/AAA mutation.