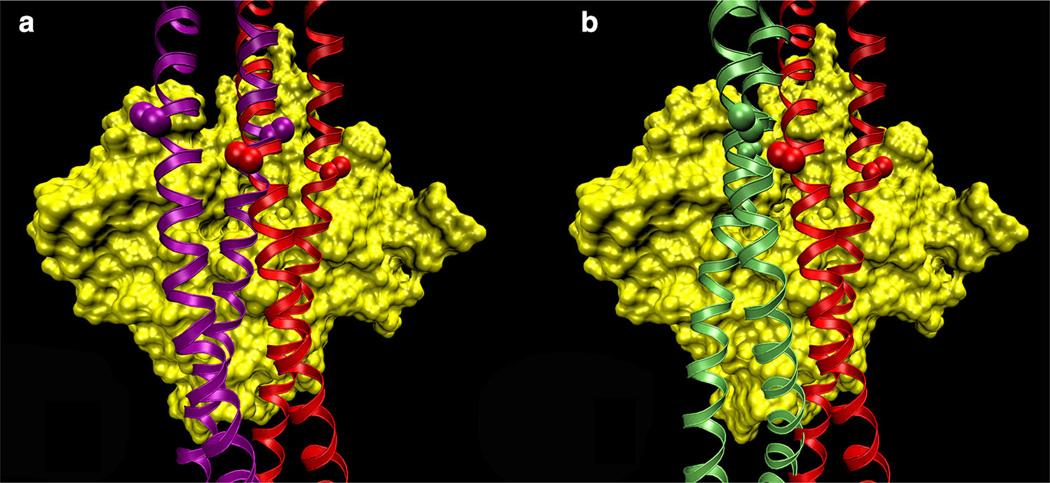
Fig. 1.
Binding-mode possibilities of tropomyosin on F-actin. Models of tropomyosin (ribbons) superposed on an actin subunit (surface rendered in yellow). a The Li et al. (2011) structure (red) was translated longitudinally and rotated azimuthally to a new position (purple), keeping the interacting-face unchanged. Note how the side chains of residues 118 (marked by spheres) are parallel to the surface of actin in both structures. b The von der Ecken et al. (2014) model (green) presents a different face to F-actin than the Li et al. (2011) model does. Note how the residue 118 side-chains are perpendicular to the surface of F-actin, thus the interacting-face is different between the two models