Figure 4.
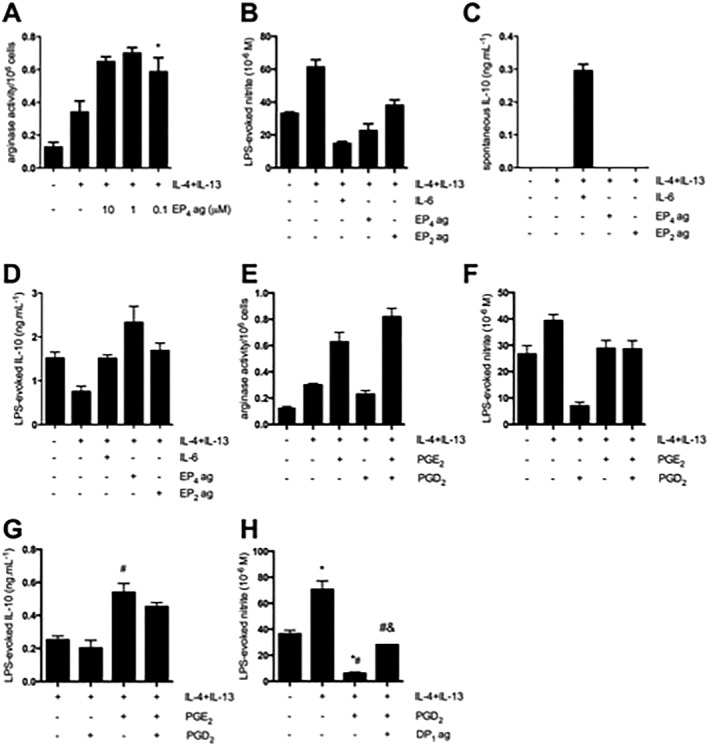
The macrophage EP4 and DP1 prostanoid receptors mediate the effects of PGE2 and PGD2 on AAMs. (A–B) Activation of the EP4 receptor using L902,688 (EP4 agonist) in the presence of IL‐4 + IL‐13 increases arginase activity (n = 3) and also suppresses LPS‐evoked nitric oxide production. Subtle suppression of nitric oxide was also observed following co‐treatment with an EP2 agonist (ONO‐AE1‐259, 10 μM, n = 3). (C–D) Activation of the EP4 receptor in the presence of IL‐4 + IL‐13 has no effect on the spontaneous production of IL‐10. In response to LPS, IL‐10 production is enhanced by the combination of IL‐4 + IL‐13 + L902,688 (n = 3). (E) Stimulation of macrophages with IL‐4 + IL‐13 and PGE2 resulted in increased arginase activity, while IL‐4 + IL‐13 + PGD2 did not increase arginase activity relative to IL‐4 + IL‐13‐treated macrophages (n = 6). (F) Stimulation of macrophages with IL‐4 + IL‐13 + PGD2 suppressed nitric oxide production in response to LPS, which was not observed with IL‐4 + IL‐13 + PGE2 (n = 3). (G) Stimulation of macrophages with IL‐4 + IL‐13 + PGE2 enhanced IL‐10 production in response to LPS (n = 6). (H) Macrophages exposed to IL‐4 + IL‐13 and a DP1 receptor agonist showed suppression of nitric oxide compared with IL‐4 + IL‐13 alone, but not to the same extent as IL‐4 + IL‐13 + PGD2 (n = 6). Data are mean ± SEM, * P < 0.05 versus control, #P < 0.05 versus IL‐4 + IL‐13, &P < 0.05 versus IL‐4 + IL‐13 + PGD2; anova followed by Tukey's post hoc test.
