Figure 6.
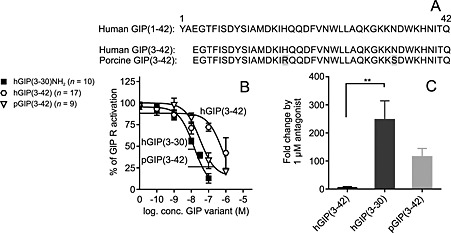
Human GIP(3–42) is a low‐potent antagonist on the human GIP receptor compared with human GIP(3–30)NH2 and porcine GIP(3–42). (A) Alignment of the truncated GIP variants. Human and porcine GIP(1–42) sequence was acquired from National Center for Biotechnology Information Protein Database. The human GIP receptor transiently transfected in COS‐7 cells was used in cAMP accumulation assay (B and C). (B) Dose–response curves of antagonists inhibited a constant amount of native GIP(1–42) corresponding to 50–80% of max receptor activation. Data shown are means ± SEM. (C) Fold change in potency of human GIP(1–42) by 1 μM antagonist. The bars display the mean fold change ± SEM, n = 4. Significance determined by multiple comparisons (one‐way ANOVA).
