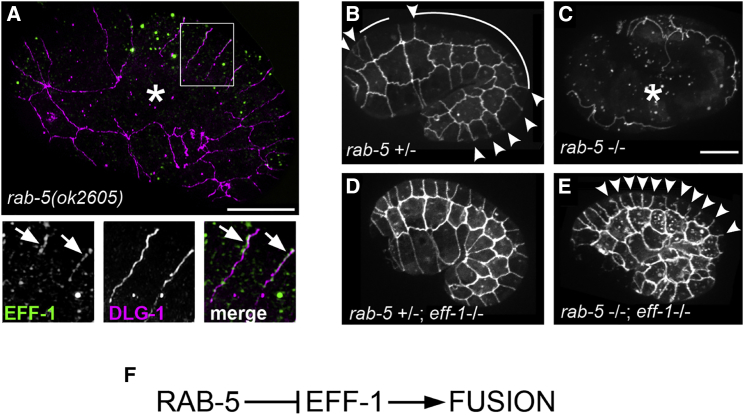
Figure 3.
Loss of rab-5 Function Induces eff-1-Mediated Ectopic Fusion
(A) Ectopic fusion (asterisk) and EFF-1 mislocalization to the plasma membrane (arrows) caused by rab-5(ok2605). Immunofluorescence with anti-EFF-1 (green) and anti-DLG-1 antibody (magenta) followed by SIM is shown. Magnifications of the inset region represent EFF-1 and DLG-1 fluorescence in separate channels and merged.
(B–E) Epistasis analysis between rab-5 and eff-1 reveals rab-5 as a negative regulator of eff-1. Fusion pattern was visualized by live imaging of junction marker DLG-1::RFP expressed in rab-5 and eff-1 single and double mutants.
(B) Heterozygous rab-5 mutant exhibits wild-type fusion. Fused cells are outlined with white stroke, junctions that will fuse later in embryogenesis (arrowheads).
(C) Hyperfusion induced by rab-5 homozygous mutation is shown (asterisk).
(D) No fusion in double rab-5(+/−); eff-1(−/−) mutant is shown.
(E) Fusion is blocked in double rab-5(−/−); eff-1(−/−) mutant, unfused junctions (arrowheads).
(F) Scheme of RAB-5-negative regulation of EFF-1 derived from the epistasis analysis. The scale bars represent 10 μm.