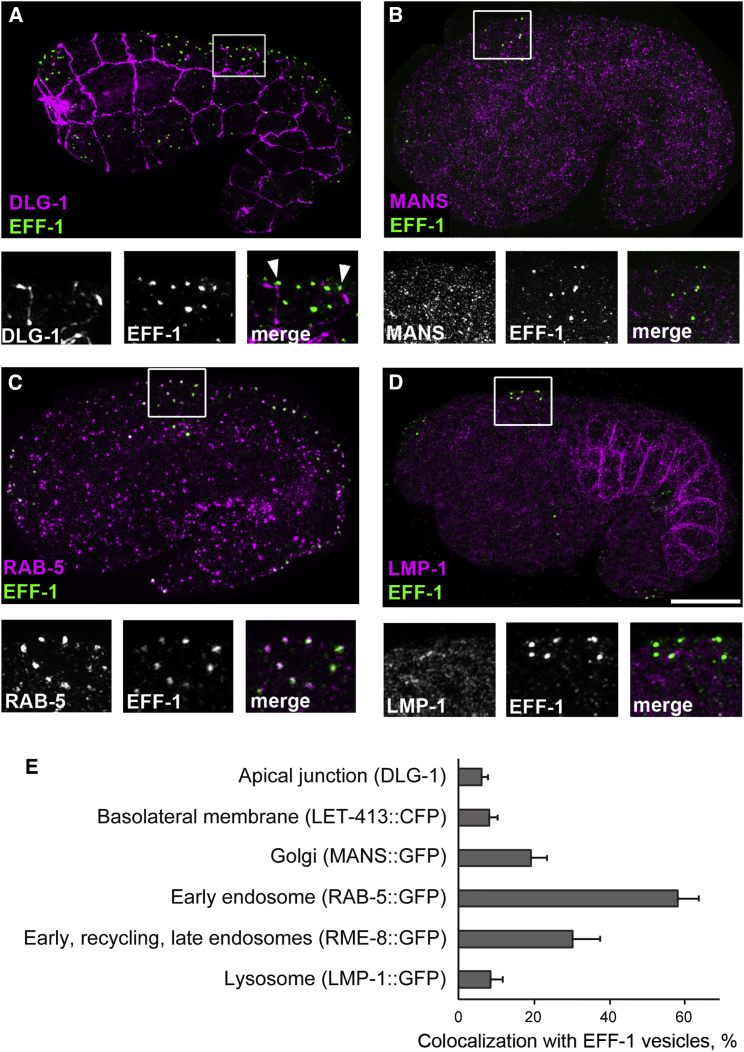
Figure 4.
EFF-1 Localization to Intracellular Compartments
(A) The localization of EFF-1 revealed by an anti-EFF-1 monoclonal antibody (green) is compared with the apical junction (anti-DLG-1 antibody, magenta) using superresolution microscopy (SIM).
(B–D) EFF-1 colocalization with stably expressed GFP-tagged markers of different membrane-bound organelles, detected with anti-GFP antibodies, magenta: Golgi complex, MANS::GFP (B); early endosomes, RAB-5::GFP (C), and lysosomes, LMP-1::GFP (D). Lower panel represents inset areas enlarged and shown in separate channels and merged.
(E) Quantification of EFF-1 colocalization with different markers represents the ratio of EFF-1 puncta that overlay the puncta of indicated marker (number of colocalized EFF-1 puncta/total number of EFF-1 puncta as percentage). Bars represent mean percentage of colocalization calculated in 5–20 embryos (100–1,000 cells) ± SEM. The colocalization above 5% is shown in the graph. The full list of intracellular markers tested, number of puncta, and number of embryos per marker are shown in Table S1. See also Figure S4. The scale bar represents 10 μm.