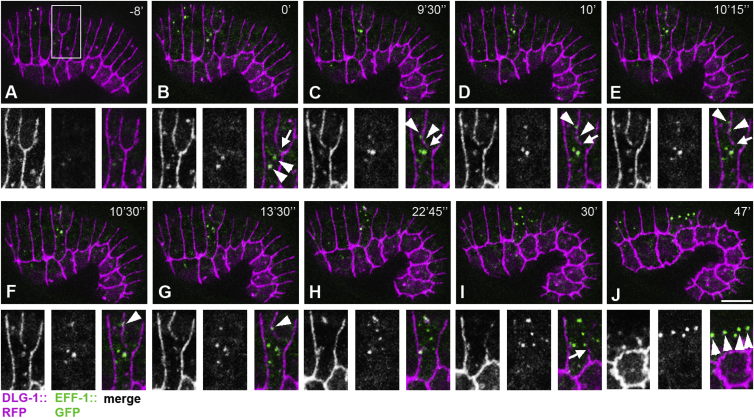
Figure 5.
The Dynamics of EFF-1::GFP during Cell Fusion
Live imaging of EFF-1::GFP (green) and apical junction marker DLG-1::RFP (magenta) in the process of dorsal fusions. Fusing cells are highlighted in (A), and higher magnification inset is shown below in separate channels: DLG-1::RFP (left); EFF-1::GFP (middle); and merged image (right panel). (B–E) Early stages of apical junction disassembly (arrows). Dynamic colocalization of EFF-1 and DLG-1 on plasma membranes (arrowheads). Time points (in minutes and seconds) of image acquisition are presented in the upper right corners. Time 0’ indicates the beginning of Movie S1.
(A) EFF-1::GFP fluorescence is barely detectable in cells that are going to fuse.
(B) EFF-1::GFP appears in the cell cytoplasm within a pair of bright vesicles (arrowheads) and diffuse where the cell junction disassembles (arrow).
(C–E) EFF-1::GFP arrives at the cell junction from both fusing cells (C, arrowheads) and move along the junction (D and E, arrowheads). Arrows mark the edge of the cell junction undergoing disassembly.
(F) EFF-1 puncta coming from opposite cells join together on the cell junction (arrowhead).
(G and H) At the end of the first dorsal cell fusion, EFF-1::GFP puncta are distributed in the cytoplasm of the syncytium.
(I) Second junction discontinuity revealing the second cell fusion (arrow).
(J) EFF-1::GFP vesicles become larger, brighter, and aligned in an anterior-posterior line (arrowheads) within the intermediate syncytium. The scale bar represents 10 μm.