Fig. 7.
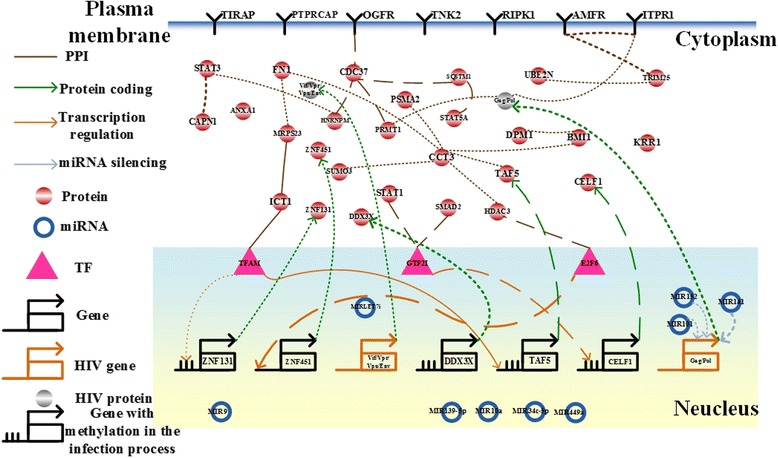
The integrated genetic and epigenetic cellular network for investigating the cellular mechanisms of normal and HIV-infected T cells at the late HIV infection stage, i.e., the virus assembly/budding stage. The associations include those in HIV-infected cells (dotted lines), normal cells (dashed lines), and both cell types (solid lines). The bold lines indicate large genetic and epigenetic regulatory effects or genetic expression. Dysregulation of MIR101, MIR141, and MIR152 to the HIV-1 Gag protein contributes to HIV-1 budding and release via DNA hypermethylation, ubiquitin transfer, and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation at the late infection stage
