Fig. 2.
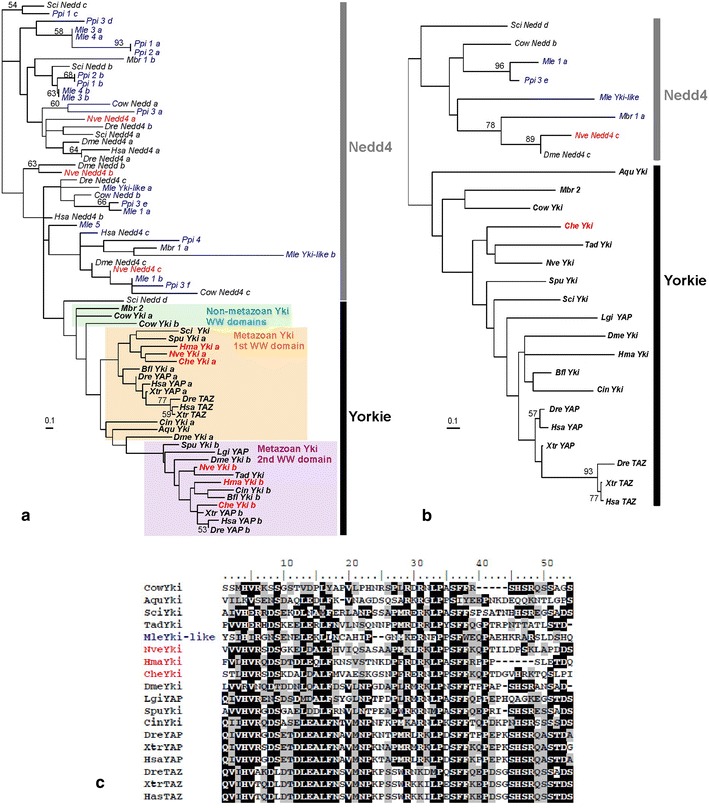
Rooted phylogenetic analyses of Yorkie sequences. a Analysis of aligned WW domains (multiple WW domains of the same protein numbered sequentially with letters: a, b, c, etc.). WW domains of Nedd4 were used to root the tree. b Combined analysis of the TBD domain and the two WW domains. In a, b sequences from ctenophores are in blue and sequences from cnidarians in red; support values are indicated next to the branches when higher than 50 %. c Alignment of the TBD domains of MleYki-like (in blue) with Yki TBD domains from various organisms (cnidarians in red). Species names are indicated by a three-letter code (see taxonomy in “Methods”): Aqu: Amphimedon queenslandica, Bfl: Branchiostoma floridae, Che: Clytia hemisphaerica, Cin: Ciona intestinalis, Cow: Capsaspora owczarzaki, Dme: Drosophila melanogaster, Dre: Danio rerio, Hma: Hydra magnipapillata, Hsa: Homo sapiens, Lgi: Lottia gigantea, Mle: Mnemiopsis leidyi, Mbr: Monosiga brevicollis, Nve: Nematostella vectensis, Ppi: Pleurobrachia pileus, Sci: Sycon ciliatum, Spu: Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, Tad: Trichoplax adhaerens, Xtr: Xenopus tropicalis. Scale bar inferred number of substitutions per site
