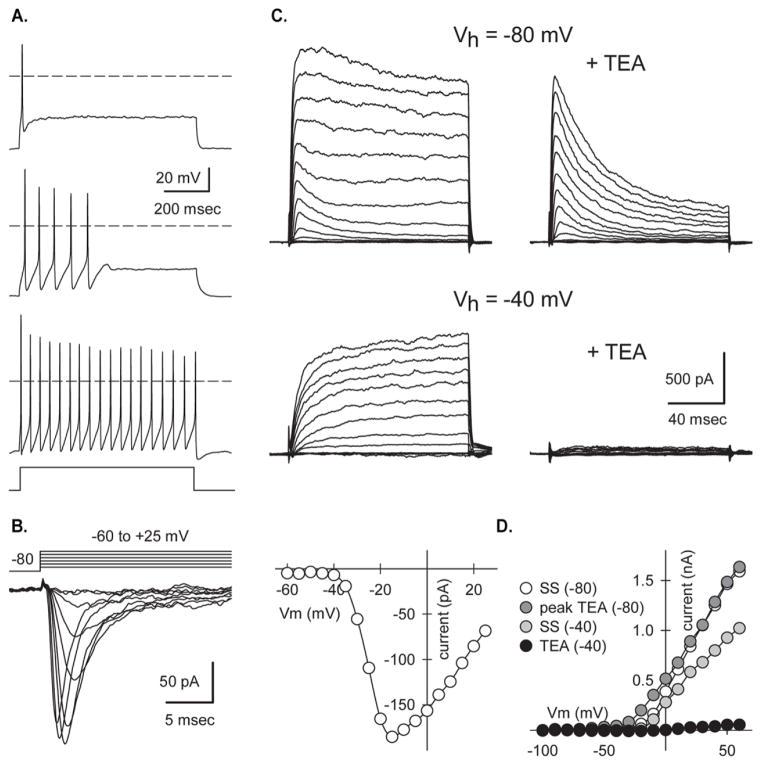
Figure 5. Action potentials and voltage-gated currents in selected Chx10-Puro cells.
(A) Action potential firing patterns recorded on d9 in 3 different selected cells stimulated with 800 msec square pulse current injections. (B) Currents mediated by voltage-gated sodium channels sensitive to tetrodotoxin (TTX) on d2 evoked by steps from a holding potential of −80 mV to test potentials ranging from −60 to +25 mV. Traces show the difference between currents recorded in the absence and presence of 0.5 μM TTX. Peak inward current plotted as a function of test potential. (C) Transient and sustained outward potassium currents on d4 evoked by 130 msec voltage steps from holding potentials of −80 mV (above) or −40 mV (below) to test potentials ranging from −100 mV to +60 mV in the presence of 0.5 μM TTX. Exposure to 30 mM tetraethylammonium (TEA) blocked the sustained current, whereas holding at −40mV inactivated the transient current. (D) Current-voltage relations for transient (peak TEA) and sustained (SS) outward currents.