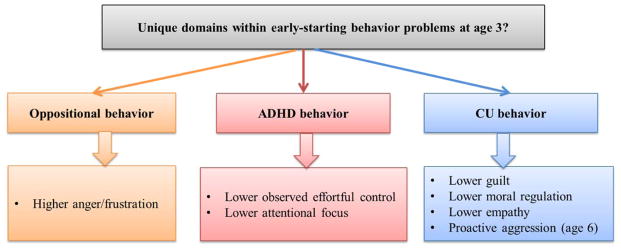
Figure 1. Unique nomological network of three domains within early childhood disruptive behavior disorder- oppositional, ADHD, and CU behavior.
Note. Figure adapted from Waller, Hyde et al. (2015). We examined associations between CU behavior, oppositional behavior, and ADHD behavior subscales and relevant socioemotional, behavioral, and cognitive correlates at age 3, controlling for overlap between subscales and child verbal IQ, age in months, and family income. ADHD scores were related to lower effortful control and attentional focus; oppositional behavior was related to higher anger/frustration; and CU behavior was related conscience deficits and uniquely predicted higher teacher-reported externalizing behavior at age 6, including higher proactive aggression. These results support the existence of unique correlates for different components of early-starting disruptive behavior. We replicated findings using cross-informant models incorporating both mother versus father reports of CU, oppositional, and ADHD behavior at age 3.