Figure 3.
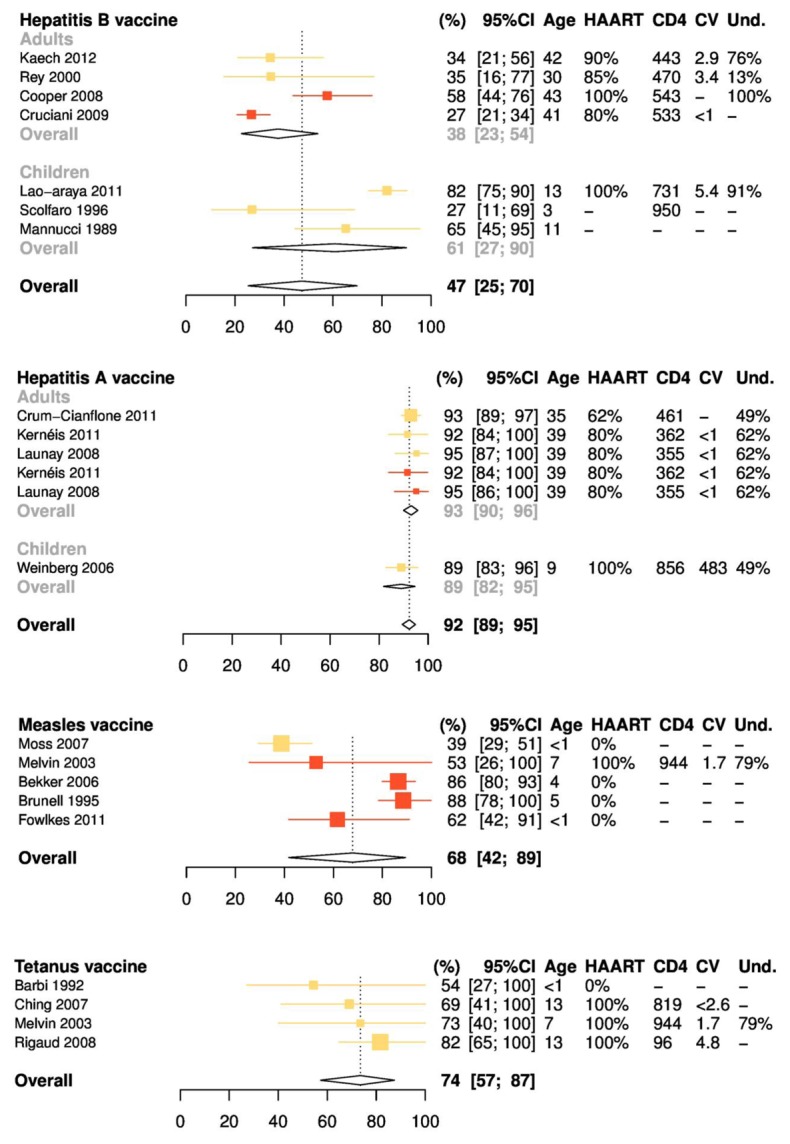
Meta-analysis of the percentages of seroprotection 2 years after the last vaccine dose, by vaccine antigen. Columns on right detail characteristics of study participants at the time of immunization, including mean or median age, percentage receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), mean or median CD4 cell count (per microliter), mean or median human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) load (log copies per milliliter), and percentage with undetectable HIV loads. Colors represent vaccination protocols. For hepatitis B, yellow symbols represent 3 intramuscular 10-μg doses (Lao-Araya et al [13] and Scolfaro et al [18]) or 3 subcutaneous 5-μg doses (Mannucci et al [14]) in children or 3 intramuscular 20-μg doses in adults (Kaech et al [12] and Rey et al [17]). Red symbols represent 3 intramuscular 40-μg doses (Cooper et al [10] and Cruciani et al [8]). Heterogeneity: Q = 121.9; P < .001; I2 = 95% [92%–97%]. For hepatitis A, yellow symbols represent 1 dose (Weinberg et al [24], Crum-Cianflone et al [21], Kernéis et al [22], and Launay et al [23]); red symbols, 2 doses (Kernéis et al [22] and Launay et al [23]). Heterogeneity: Q = 2.9; P = .71; I2 = 0% [0%–57%]. For measles, yellow symbols represent 1 dose (Moss et al [31]); red symbols, 2 doses (Melvin and Mohan [30], Bekker et al [26], Brunell et al [27], and Fowlkes et al [29]). Heterogeneity: Q = 25.6; P < .001; I2 = 84% [65%–93%]. For tetanus, yellow symbols represent 2–5 doses plus boosters, according to local practices. Heterogeneity: Q = 2.5; P = .48; I2 = 0% [0%–81.3%].
