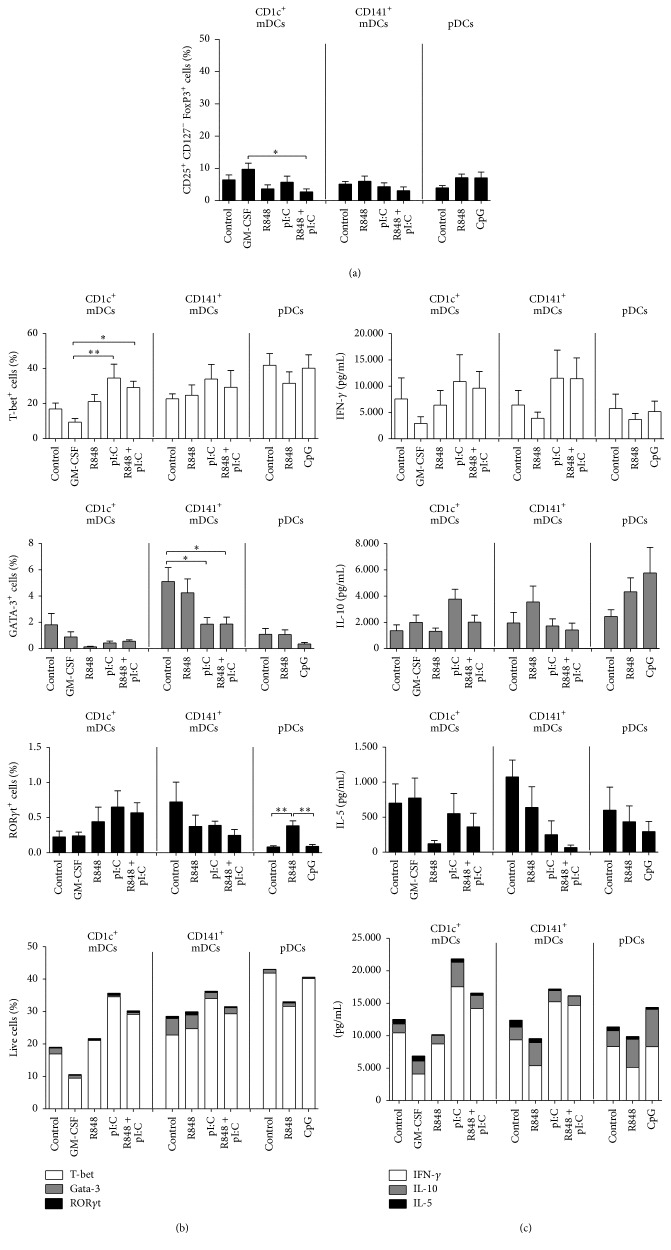
Figure 4.
Mature human DC subsets can skew naive CD4+ T cells towards Th1 phenotype and do not induce a big population of Tregs. Human blood DCs were incubated with the indicated stimuli. The next day, allogeneic naive CD4+ T cells were added to the DCs together with a low concentration of the superantigen SEB (10 pg/mL) and cultured until resting (11–13 days). (a) These CD4+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for presence of a Treg population (CD25+CD127−FoxP3+ CD4+ T cells) (n ≥ 5). (b) The cells were also stained for the expression of transcription factors T-bet, Gata-3, and RORγt. In the lower panel, all three transcription factors are depicted in a single bar graph (mean value for each). (c) Furthermore, 5 × 104 of these CD4+ T cells were restimulated for 24 hrs with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Supernatants were analyzed for IL-5, IL-10, and IFN-γ by sandwich ELISA (n ≥ 4). The bar graphs show mean cytokine production ± SEM. In the lower panel, all three cytokines are depicted in a single bar graph (mean value for each cytokine). Significance comparing different conditions of the same subset was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's testing (a and c), by a 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey testing or a paired t-test (b) (∗ P < .05; ∗∗ P < .01).