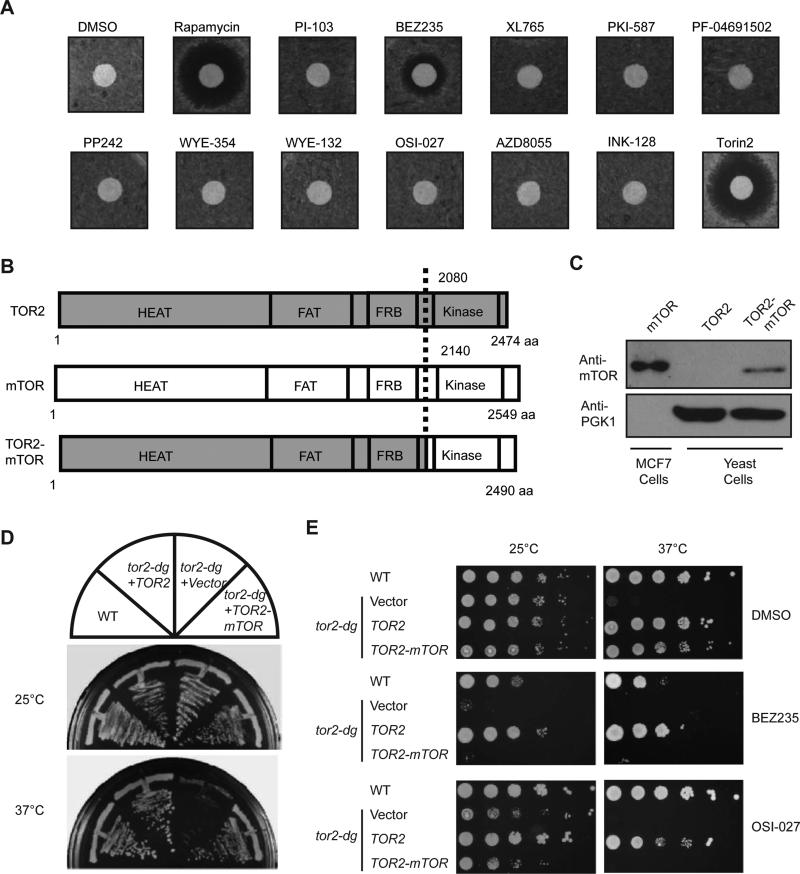
Figure 1. Developing a yeast system to assay for mTOR kinase inhibition.
(A) Wild type (WT) yeast cells were spread onto YPD plates and tested for sensitivity to structurally diverse mTOR kinase inhibitors by disc halo assay. Rapamycin was used as a positive control.
(B) The N-terminus of TOR2 (1-2080 aa) was fused in frame with mTOR kinase domain (2140-2549 aa). The TOR2-mTOR fusion is expressed under the control of TOR2 promoter in a centromeric plasmid.
(C) Yeast strain expressing WT TOR2 or TOR2-mTOR fusion was analyzed for expression by immunoblot with an antibody specific for mTOR kinase domain. PGK1 was used as a loading control and extracts from MCF7 breast cells were used as a positive control for mTOR.
(D) TOR2-mTOR fusion was expressed in tor2-dg and tested for its ability to complement TOR2 function by growth at permissive and restrictive temperatures.
(E) tor2-dg cells expressing TOR2 or TOR2-mTOR were serially diluted by 10-fold and tested for drug sensitivity on plates containing BEZ235 and OSI-027.