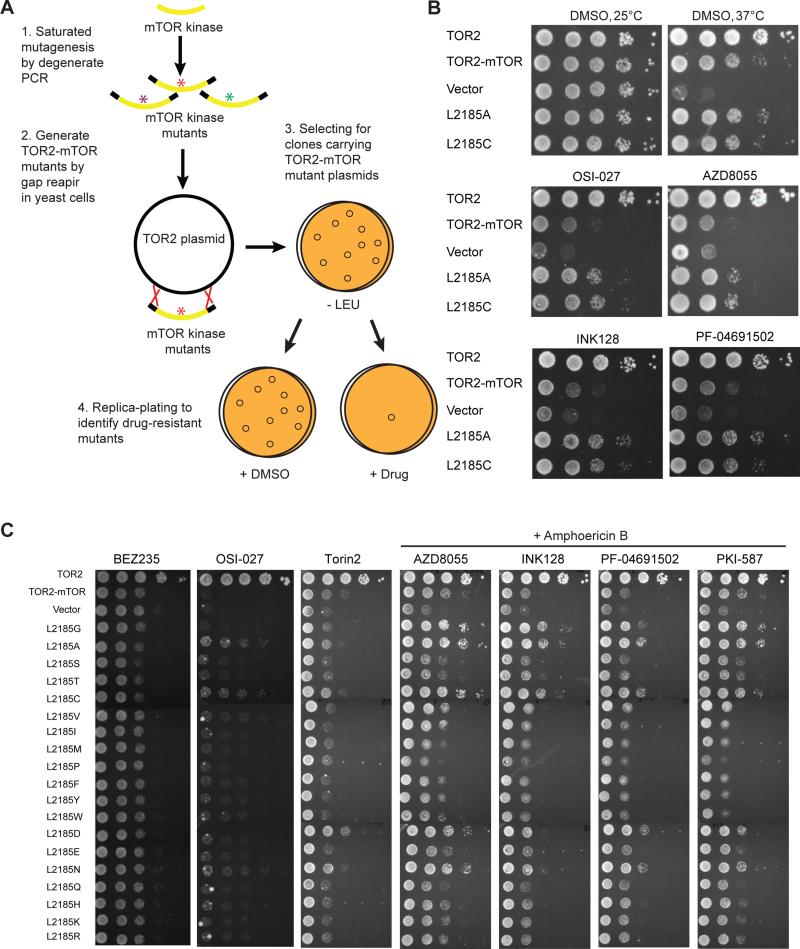
Figure 4. Identification of a hotspot for drug-resistant mutations in mTOR kinase domain.
(A) Scheme of a yeast-based screen for drug-resistant mutations in mTOR kinase domain. mTOR kinase domain is amplified by error-prone PCR to generate randomized mutations, which is then recombined in frame into the TOR2-mTOR plasmid by gap-repair in tor2-dg cells, and is selected on SC-leucine minus plates. Replica plating is then made onto SC-leucine plates containing DMSO or mTOR kinase inhibitor for selection of drug resistant clones.
(B) tor2-dg cells expressing WT or mutant TOR2-mTOR were serially diluted by 10-fold and assayed for sensitivity to different mTOR kinase inhibitors in the presence of amphotericin B. Vector and TOR2 were used as controls. Drug resistant assay was performed at 37°C in the presence of amphotericin B (except OSI-027).
(C) Systematic mutational analysis of L2185 on drug resistance. tor2-dg cells expressing WT or mutant TOR2-mTOR carrying all possible mutations at L2185 were serially diluted by 10-fold and tested for sensitivity to different mTOR kinase inhibitors at 37°C. AZD8055, BEZ235, INK128, PF-04691502 and PKI-587 were supplemented with amphotericin B.