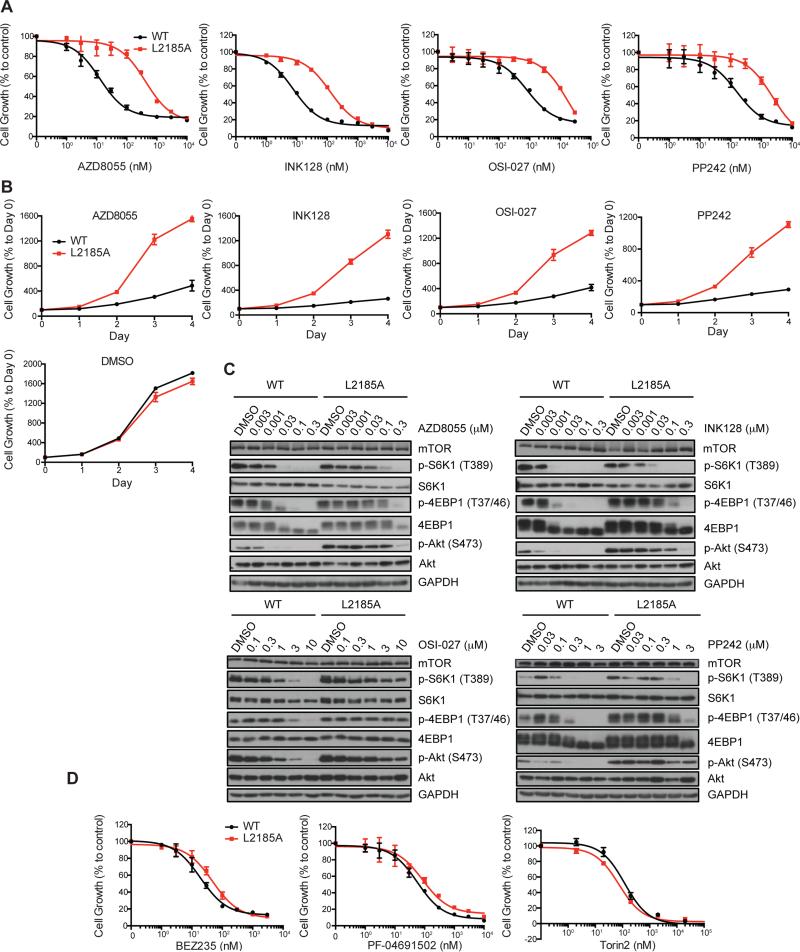
Figure 5. L2185A mutation confers resistance to mTOR kinase inhibitors in colorectal cancer models.
(A) SW480 cells carrying homozygous WT mTOR or L2185A mutant alleles were treated with various concentrations of AZD8055, INK-128, OSI-027 and PP242 for 2 day. Growth of SW480 cells was measured by SRB assay. Data represent means ± SD in three independent experiments.
(B) SW480 cells carrying homozygous WT and L2185A mutant mTOR allele were treated with a single dose of AZD8055 (100 nM), INK-128 (100nM), OSI-027 (6,000 nM), and PP242 (2,000 nM) for different times. Cell growth was measured by SRB assay. The drug carrier DMSO was used as a control. Data represent means ± SD in three independent experiments.
(C) SW480 cells carrying homozygous WT and L2185A mutant mTOR were treated with various concentrations of INK-128, OSI-027, AZD8055 and PP242 for 1 hr. The effect on the level of P-S6K, S6K, P-4E-BP1, 4EB-P1, P-AKT and AKT was analyzed by immunoblot.
(D) SW480 cells carrying homozygous WT and L2185A mutant mTOR alleles were treated with various concentrations of BEZ235, PF-0691502 and Torin2 for 2 day. The growth of SW480 cells was measured by SRB assay. Data represent means ± SD in three independent experiments.