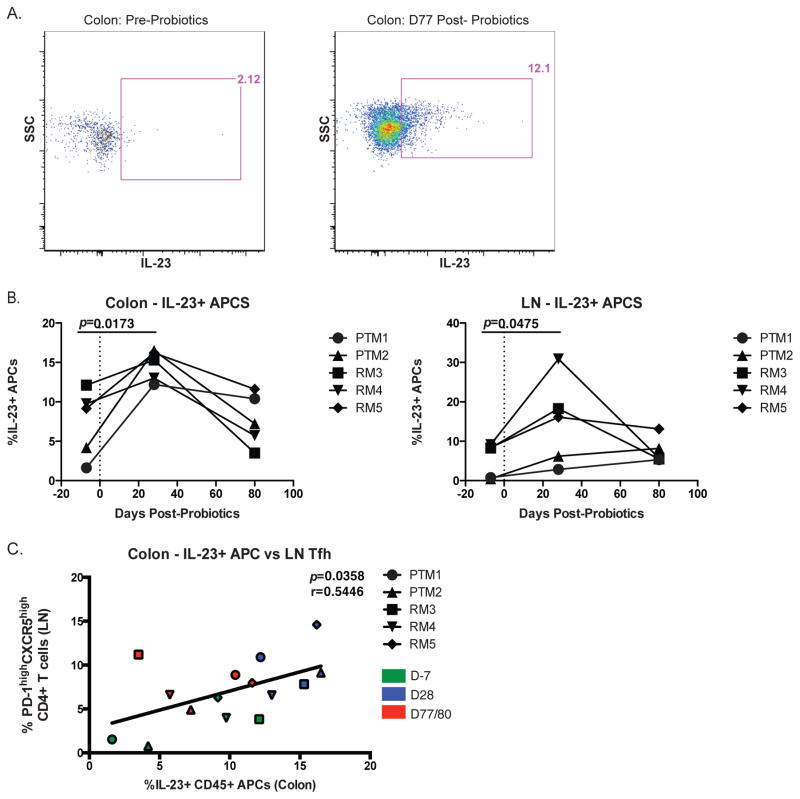
Fig. 4.
Increased frequency of IL-23+ APC in the colon and LN post-PBio therapy. (A) Representative staining demonstrating the IL-23+ APC population in the colon pre-PBio (left panel) and post-PBio (right panel). Cells were identified by first gating on lymphocytes and excluding doublets using FSC and SSC properties and removing dead cells with an Aqua Live/Dead viability dye. The frequency of IL-23+ APCs within this subset was then determined by gating on CD45+HLA-DR+ cells. (B) Percentage of IL-23+ APC in the colon (left panel) and LN (right panel) at all time-points. Each animal is represented by a different symbol. Statistical significance between the two post-PBio time-points (d28 or d77/80) and the pre-PBio time-point (d−7) was calculated using a paired t test. (C) Correlation between colon IL-23+ APC frequencies and LN Tfh frequencies at all time-points. Each animal is represented by a different symbol (n=5). Each experiment was performed once per animal per time-point. D−7 time-points are in green, d28 time-points are blue and d77/80 time-points are red. Statistical significance of the correlation was calculated using a Pearson’s test.