Fig. (3).
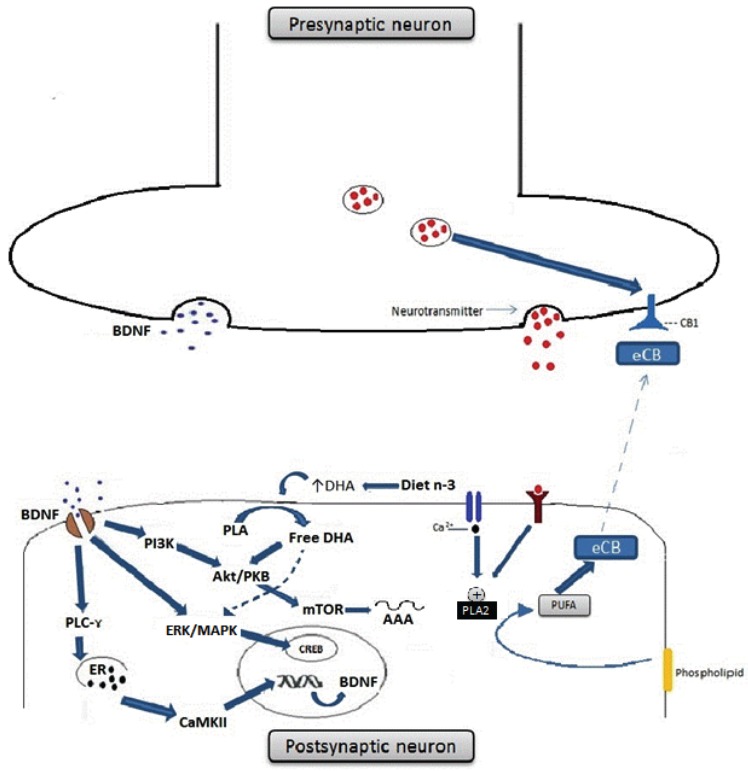
Omega-3 fatty acids enhance BDNF synthesis and signalling in neurons and also influence cannabinoid-mediated synaptic plasticity. (A) BDNF binds cognate TrKB receptors and activates PLC-γ, ERK/MAPK and Akt/PKB intracellular signalling pathways. Activation of PLC-γ leads to the release of calcium from the endoplasmatic reticulum and to the activation of CAMKII, which phosphorylates CREB and activates gene transcription. Activation of ERK/MAPK pathway also regulates transcription through CREB phosphorylation, whereas PI3K phosphorylates and activates Akt/PKB and mTOR, regulating translation. DHA enhances neurotrophic signalling by the PI3K/Akt BDNF signal transduction pathway. DHA also activates the MAPK pathway; activated MAPK then phosphorylates CREB which translocates into the nucleus and activates BDNF gene transcription. (B) Endocannabinoids (eCBs) are signalling lipids produced from PUFAs present in membrane phospholipids. PUFAs are released from the postsynaptic membrane by phospholipase A2 (PLA2) in response to neuronal activation. eCB released in the synaptic cleft can bind presynaptic cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) on the presynaptic neuron. Activation of CB1 leads to inhibition of neurotransmitter release and synaptic activity. In rodents that are fed a n3-PUFA enriched diet, such eCB-mediated long-term depression (LTD) is inhibited at excitatory synapses, whereas rodents fed a diet chronically low in n-3 PUFAs has this form of eCB-mediated synaptic plasticity specifically interrupted. Abbreviations: BDNF- brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CAMKII- Calciumcalmodulin kinase II; CREB- cAMP-response element-binding protein; DHA-Docosahexaenoic acid; n-3-n-3 PUFAs; ERK- extracellularsignal- regulated kinases; MAPK- Mitogen-activated protein kinases; PI3K- Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt/PKB- Protein kinase B; mTORMechanistic target of rapamycin.
