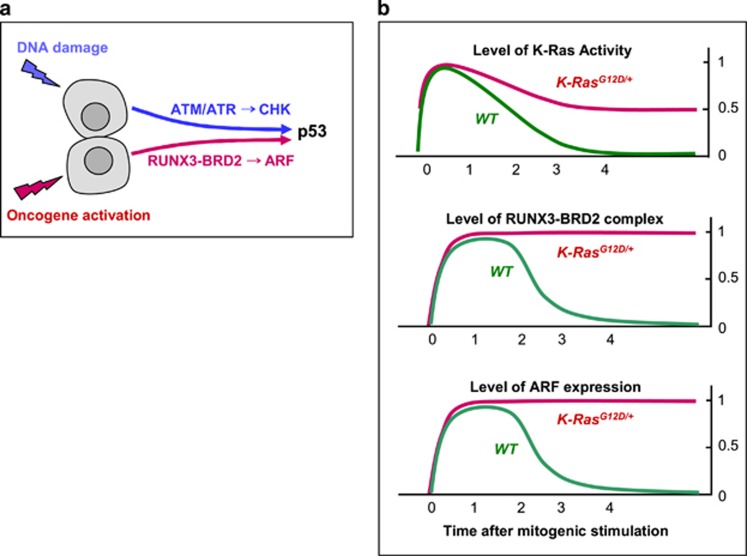
Figure 3.
p53 tumor-suppressor pathways. (a) Two major pathways trigger p53 activation. (1) DNA damage stress is sensed by the ATM/ATR kinases, which activate the CHK1/CHK2 kinases, which in turn stabilize p53. Aberrant oncogene activation is sensed by the RUNX3–BRD2 complex, which induces expression of ARF, which in turn inactivates HDM2 and thereby stabilizes p53. (b) Mechanism for sensing constitutive RAS activation. Normal RAS activity is downregulated to the basal level soon after mitogenic stimulation (top panel, green line). Although RAS is activated, the RUNX3–BRD2 complex is formed (middle panel, green line) and ARF expression is induced (bottom panel, green line). In normal cells, RUNX3–BRD2 complex formation and ARF expression occurs for only a short time (1–3 h after mitogenic stimulation) and disappears when RAS activity is downregulated. However, heterozygous mutation of RAS results in maintenance of 50% of the maximum level of RAS activity. This persistent RAS activity maintains the RUNX3–BRD2 complex and ARF expression until the G1/S check point.