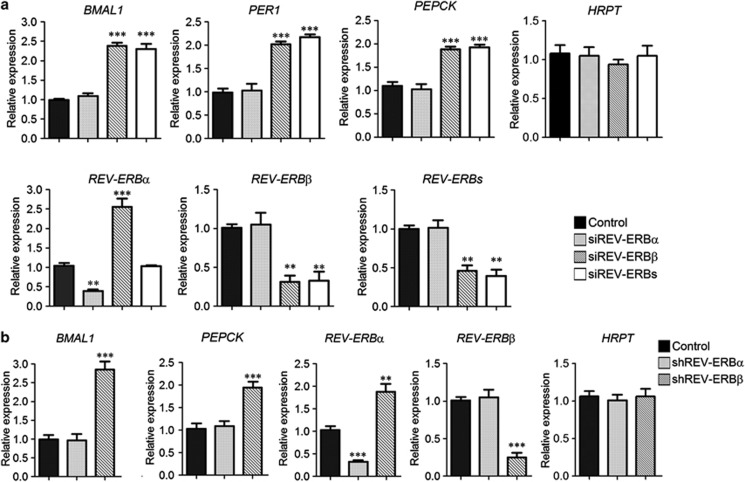
Figure 2.
REV-ERBβ overrepresentation corresponds to a preponderant functional role in REV-ERB-mediated transcriptional regulation. (a) The expression of the circadian (BMAL1, PER1) and metabolic (PEPCK) REV-ERB-regulated genes was analyzed in BT-474 cells 72 h after transfection with pooled siRNA sequences against REV-ERBα (siREV-ERBα), REV-ERBβ (siREV-ERBβ) and both REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ (siREV-ERBs), with a non-targeting pool as a negative control (Control). Relative expression was determined by quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR (qRT–PCR) using GAPDH for normalization. HRPT expression is reported as representative of a REV-ERB-independent gene. The effect of REV-ERBs silencing on the two nuclear receptor variants was also evaluated. Levels of total REV-ERB transcripts (REV-ERBα plus REV-ERBβ) is indicated as REV-ERBs. Shown as mean±s.e.m., n=3. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, siRNA target sequences versus control. (b) BT-474 cells were transfected with vectors co-expressing a GFP protein with shRNA sequences against a non-targeting (Control), REV-ERBα (shREV-ERBα), REV-ERBβ (shREV-ERBβ) genes. Forty eight hours post-transfection, GFP-positive cells were sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and processed for qRT–PCR analysis to evaluate the expression of REV-ERB-regulated genes. The relative expression was determined using GAPDH for normalization. HRPT expression is reported as representative of a REV-ERB-independent gene. Data are shown as mean±s.e.m., n=3. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, shRNA samples versus control.