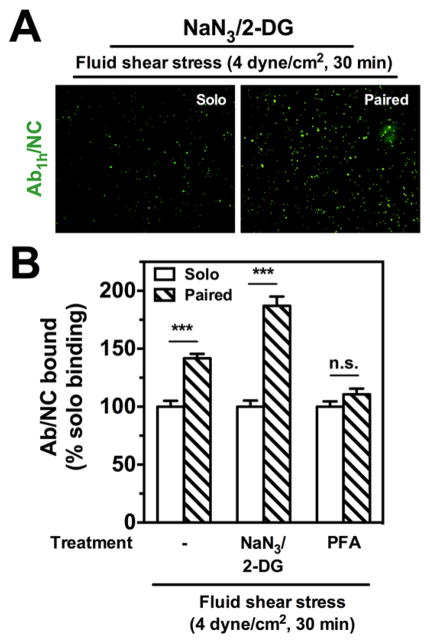
Figure 3.
Blocking internalization does not abrogate stimulated endothelial binding of anti-PECAMAb1h/NCs. (A) Under flow conditions of acute fluid shear stress (4 dyn/cm2, 30 min), fluorescence images show endothelial HUVEC binding of Ab1h/NCs (green) with paired Ab2h pretreatment (20 nM) is increased compared to solo IgG pretreatment with NaN3/2-DG (5 mM). (B) Despite blocking of internalization with NaN3/2-DG, Ab1h/NC binding is significantly increased by 87% over solo binding under flow. For cells prefixed with paraformaldehyde (PFA, 1%, 10 min) and then subjected to flow, the enhanced endothelial binding of Ab1h/ NCs (200 Abs/NC) with free Ab2h preincubation (20 nM) is completely abolished to control IgG levels. The number of EC bound fluorescent particles in each image filed (104 μm2) was quantified by fluorescence microscopy under flow conditions and presented as % solo binding. Data are mean±SE (n = 8). n.s., P > 0.05. Open bars show NC binding with solo treatment; hashed bars show NC binding with paired free Ab treatment.