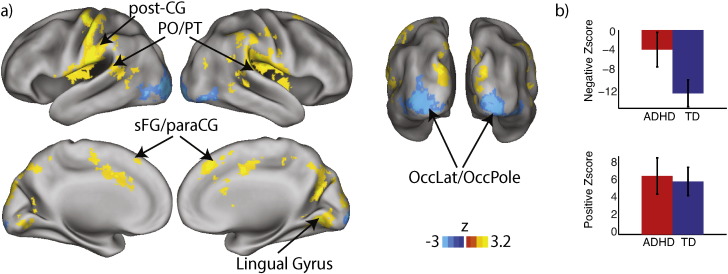
Fig. 4.
EEG-fMRI results: alpha ERD & neural activity. Greater alpha ERD during SWM encoding predicted (a) increases of activity in bilateral lateral occipital cortex (OccLat) and occipital pole (OccPole), and with decreases of activity in post-central gyrus (post-CG), planum temporale (PT), posterior operculum (PO), and superior frontal gyrus (sFG) extending into paracingulate cortex (paraCG). The mean activation effect across occipital cortices was significantly stronger in the TD group than in the ADHD group (b, top), whereas the group difference was not significant for the activation decreases associated with alpha ERD (b, bottom). TD, typically developing; ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Parametric maps thresholded at cluster height of z > 2.3, p < .05, whole-brain corrected for multiple comparisons.