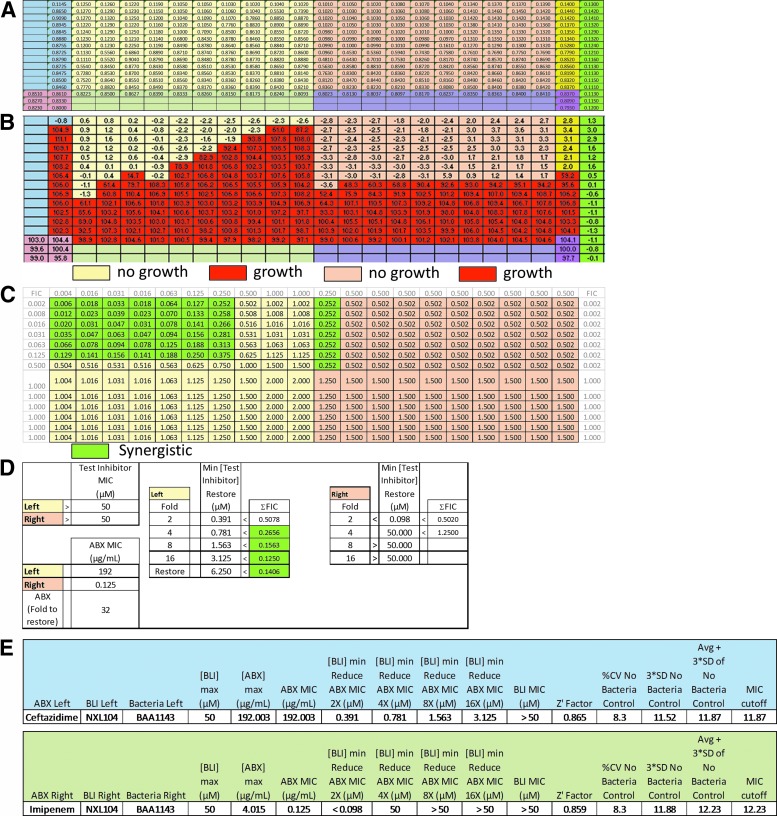
Fig. 2.
The Synergy RunTool displaying separate areas of interpretation. (A) The RunTool first imports raw data and displays it overlaid with regions color coded for compound and control allocation. (B) Data are then normalized and MICs determined per the methods described implementing user-defined controls. Bacterial growth versus no growth is automatically assigned the heat map colors depicted biased upon the automatically interpreted MIC values. (C) The same application calculates the ΣFIC using the formula described in the manuscript. The value calculated in each well is used to determine whether the compound is synergistic with the antibiotic assigning a shade of green if it is. A value of ≤0.5 means the compound synergizes with the antibiotic. (D) 384-wpf synergy testing yields two sets of data per plate pertaining to the left and right side of the plate. Results are shown in a color-coded table that quickly allows determination of Test Inhibitor MIC (alone), ABX MIC (alone), synergy shown as the fold potentiation, Min [Test Inhibitor] Restore = the μM concentration required to obtain its designated fold or full restoration of ABX efficacy, and the ΣFIC. Again, a synergistic result is shaded green. In the “Left” result, full restoration of ABX efficacy was achieved. (E) The statistics generated using the Synergy RunTool and also corresponding to the data generated as part of the illustration above. Separate statistics are calculated for each side of the plate. BLI Left is the compound tested in columns 1–12 of the assay plate and BLI Right is the bacteria tested in columns 13–23 of the assay plate. The chart shows values for the maximum BLI (inhibitor) concentration tested, maximum antibiotic (ABX) concentration, and the ABX MIC. The Synergy RunTool also calculates the [BLI]MIN needed to reduce ABX MIC by 2-, 4-, 8-, or 16-fold and the Z′ which determines assay quality as previously discussed. The MIC cutoff is shown and is determined as the sum of 3 × SD plus the average of the no bacteria control, as previously described in the text. All of these data are readily archived in the Scripps database for the ease of access by medicinal chemists. ΣFIC, Total Fractional Inhibitory Concentration.