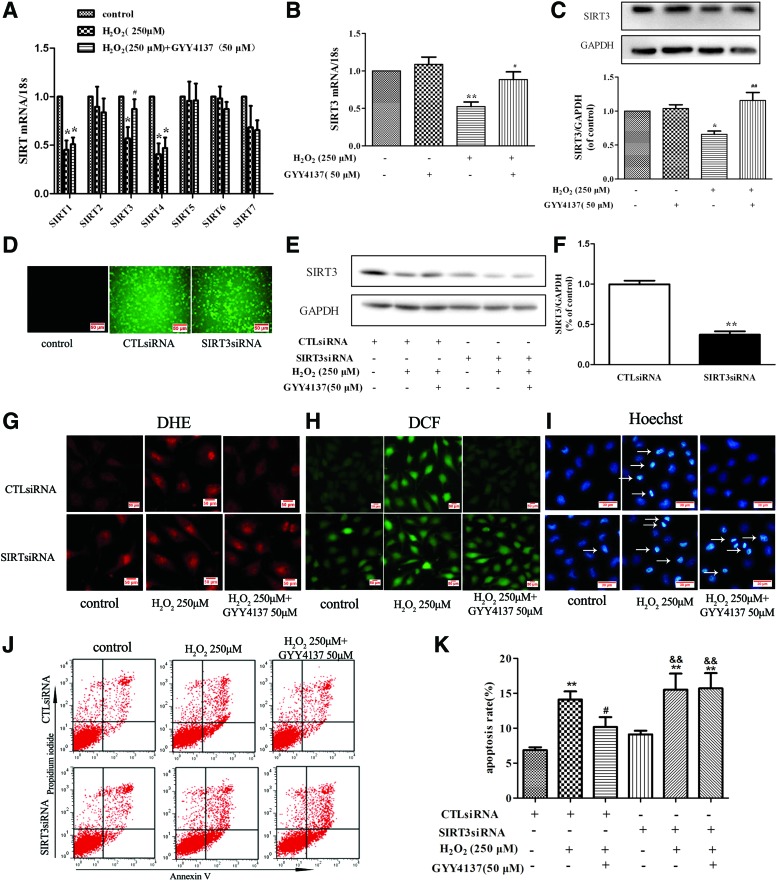
FIG. 4.
Role of SIRT3 in H2S-mediated protection of endothelial cell injury by H2O2. (A, B) EA.hy926 endothelial cells were pretreated with GYY4137 (50 μM) for 4 h before H2O2 (250 μM, 4 h). Quantification of SIRT family (SIRT1 to SIRT7) mRNA expression was determined by real-time PCR. *p < 0.05 versus control, #p < 0.05 versus the H2O2-treated group, n = 6–7. (C) Representative examples of Western blots and quantification of SIRT3 protein. *p < 0.05 versus control, ##p < 0.01 versus the H2O2-treated group, n = 5. (D) EA.hy926 endothelial cells were transfected with SIRT3-specific siRNA (SIRT3siRNA) or a nonspecific control siRNA (CTLsiRNA). Transfection efficiency was assessed by immunofluorescence. (E, F) Representative examples of Western blots and quantification of SIRT3 after transfection. **p < 0.01 versus CTLsiRNA, n = 6. Transfected with CTLsiRNA or SIRT3siRNA for 24 h, EA.hy926 endothelial cells were exposed to H2O2 (250 μM, 4 h) after pretreatment with GYY4137 (50 μM) for 4 h, (G, H) ROS in endothelial cells was examined by DHE and DCFH-DA staining, and (I) apoptosis in endothelial cells was detected with Hoechst 33342 staining, white arrows indicate the apoptotic cells. (J, K) Cells were stained with Annexin V/PI and apoptotic rates were analyzed by flow cytometry. **p < 0.01 versus CTLsiRNA transfection, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus the H2O2-treated group with CTLsiRNA transfection, &&p < 0.01 versus SIRT3siRNA transfection, n = 5. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars