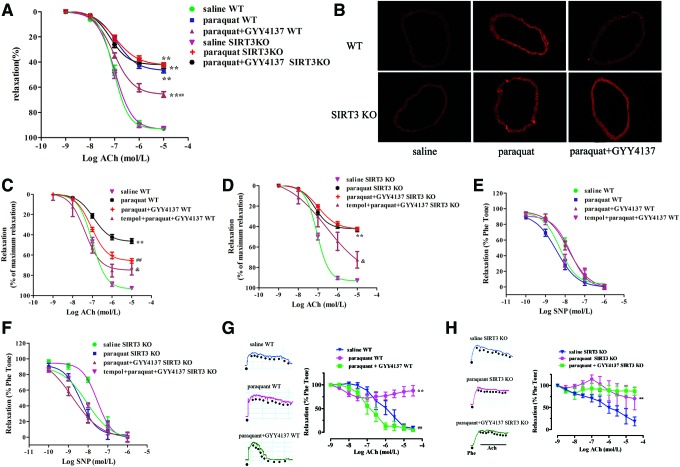
FIG. 7.
Effects of H2S on vasorelaxation in SIRT3 KO mice. (A) WT or SIRT3 KO mice were injected with either paraquat (50 mg/kg, i.p) or saline 1 h before either GYY4137 (133 μM/kg, ip) or saline. Mice were killed and aortic segments were removed 24 h thereafter. Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation to acetylcholine of precontracted aortic sections was assessed. **p < 0.01 versus the saline-treated group of the same genotype, ##p < 0.01 versus the paraquat-treated group of the same genotype, n = 6. (B) DHE staining of aorta for superoxide production (n = 4). (C, D) Above aortic segments were preincubated with tempol (1 mM) for 30 min, then endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation to acetylcholine of precontracted aortic sections was assessed. **p < 0.01 versus the saline-treated group of the same genotype, ##p < 0.01 versus the paraquat-treated group of the same genotype, &p < 0.05 versus paraquat- and GYY4137-treated groups of the same genotype, n = 6. (E, F) Vasorelaxation to SNP of precontracted aortic sections was assessed. (G, H) Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in small mesenteric artery to acetylcholine of precontracted aortic sections was assessed. **p < 0.01 versus the saline-treated group of the same genotype, ##p < 0.01 versus only the paraquat-treated group of the same genotype, n = 4–6. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars