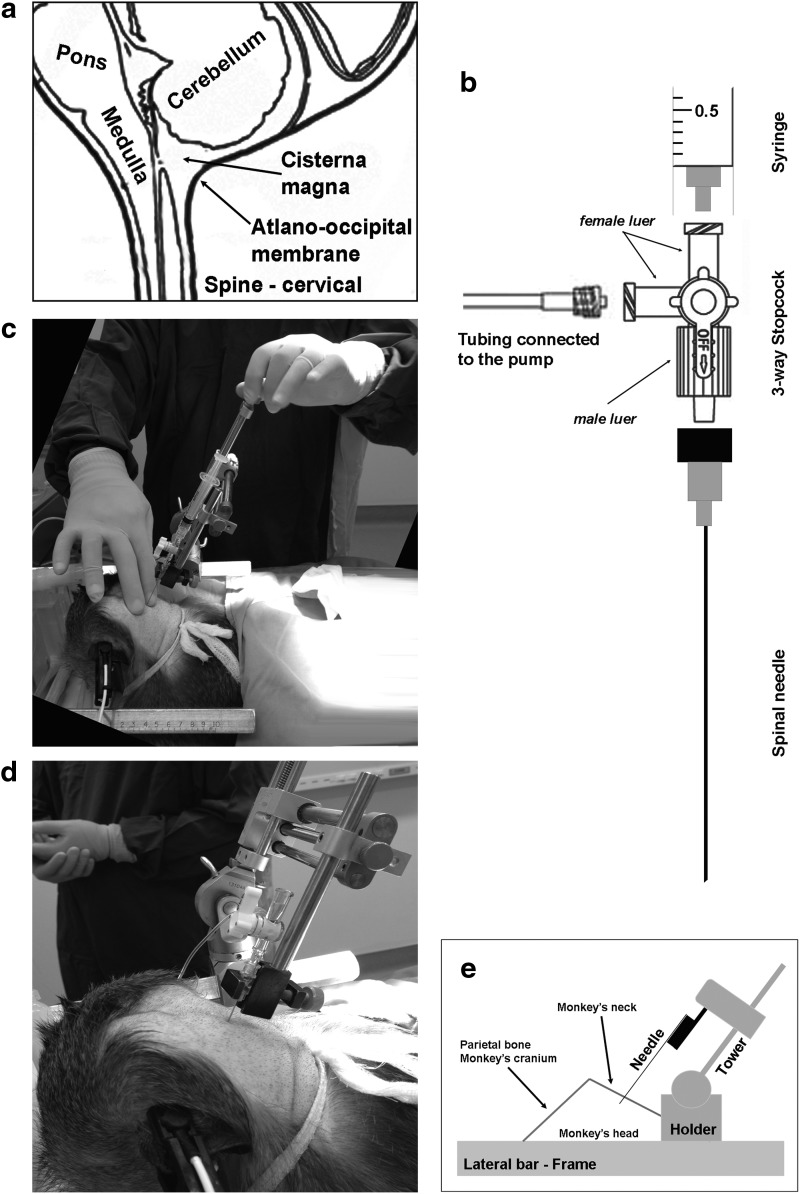
Figure 1.
Stereotactic-guided injection into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through cerebellomedullary cistern. (a) Sagittal axis illustration showing the main anatomical structures that surround cisterna magna. (b) Schematic representation of all components that comprise the injection port used during cisterna magna delivery. (c) Once the injection port is secured in the holder, the atlanto-occipital gap in the craniocervical junction is identified by palpation and the needle is manually guided to the target. (d) Needle is slowly introduced through the atlanto-occipital membrane until clear CSF comes up to the syringe. Then, the 3-way stopcock is opened to the loading line to allow vector infusion by means of a pump. (e) Based on monkey's head position in the frame, stereotactic arm might be repositioned. Gently flexed neck in prone position is recommended, and will require an angle (∼33° to ∼45°) to reach a perpendicular plane to the back of the monkey's head.