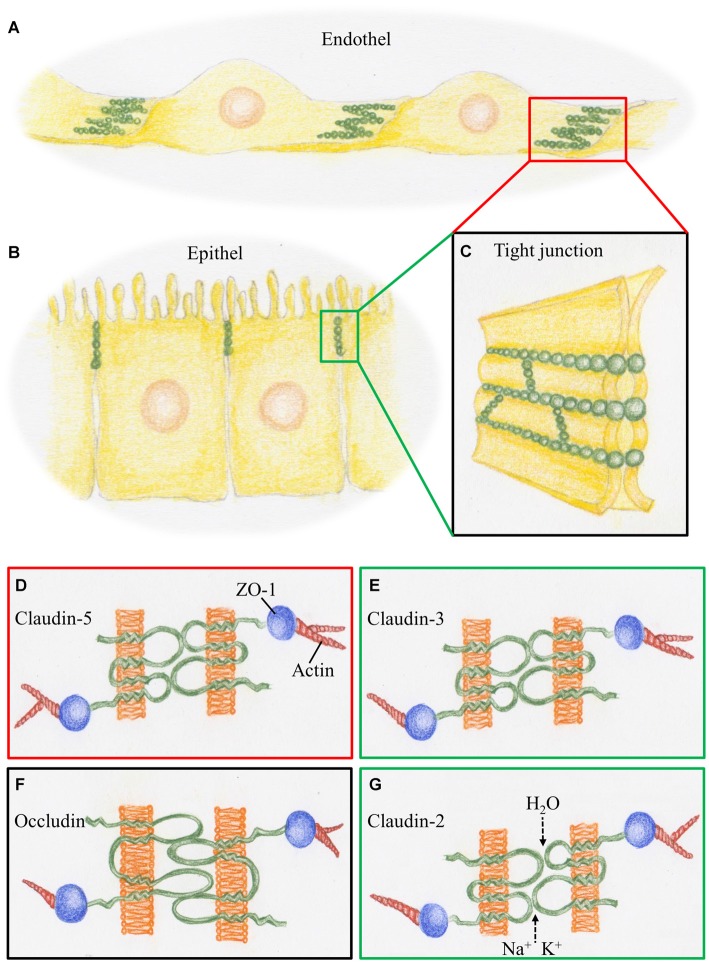
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of tight junctions (TJs) constituting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the BCSFB. (A) At the cerebral blood vessels TJ strands (green) are arranged at the overlapping parts of neighboring endothelial cells. (B) At the choroid plexus, TJ strands are arranged at the apical parts of the epithelial cells. (C) TJ strands connecting neighboring cell membranes prevent intercellular transport. (D) The BBB, represented by the red box, is characterized by claudin-5, a phosphoprotein with four transmembrane domains. It is linked via the scaffolding protein ZO1 to proteins of the cytoskeleton such as actin. (E) The BCSFB, represented by the green box, is characterized by claudin-3, which acts as a sealant, as does claudin-5. (F) Occludin, a tetra span transmembrane protein with two large extracellular loops is a obligatory member of TJ strands, as presented by the black box. (G) Claudin-2, a member of the TJs in BCSFB, is a paracellular H2O and cation channel.