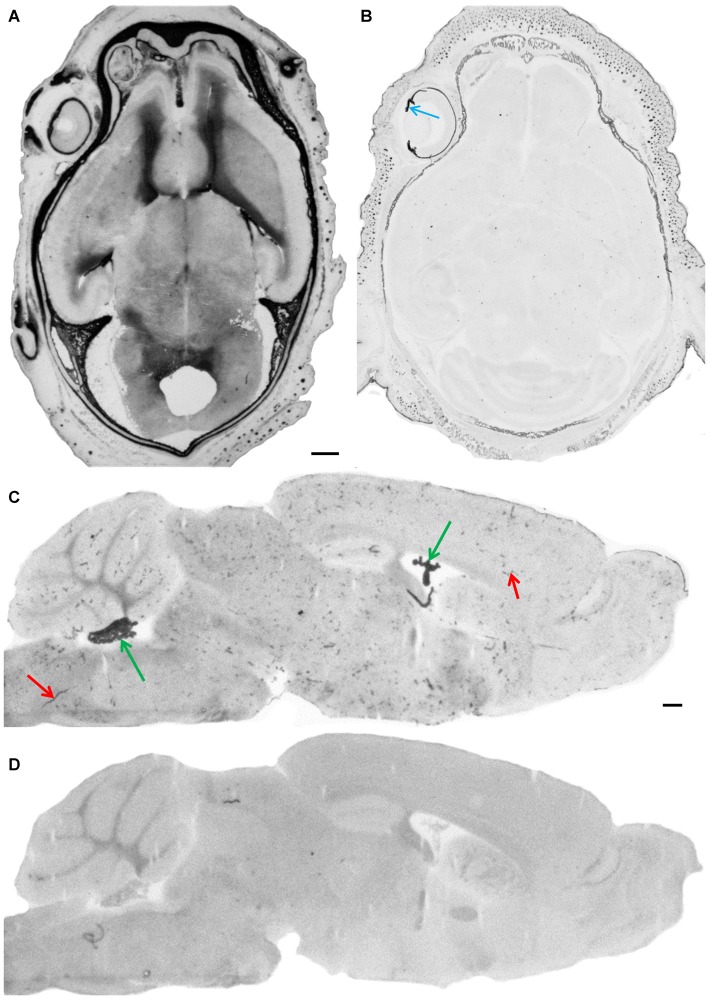
Figure 2.
Endogenous alkaline phosphatase activity and its blockage. After fixation of cryosections under standard conditions (4% paraformaldehyde/PBS pH 7.4) intense staining of AP in meninges and in the parenchyma of developing brain is shown in a horizontal section through the whole head of an E18 embryo (A). In the adult brain, AP staining is observed in choroid plexus (green arrows) and in blood vessels (red arrows) as shown here in a parasagittal section (C). Cryosections under alkaline fixation condition in the presence of EDTA (4% paraformaldehyde/20 mM Na-EDTA, pH 11.0), completely inactivates endogenous alkaline phosphatase activities in the embryonic head (B), where only pigmented structures such as the iris—see blue arrow—and the choroid of the eye bulb give a dark appearance and in the adult brain (D). Scale bar = 0.5 mm in (A) applies also for (B–D).