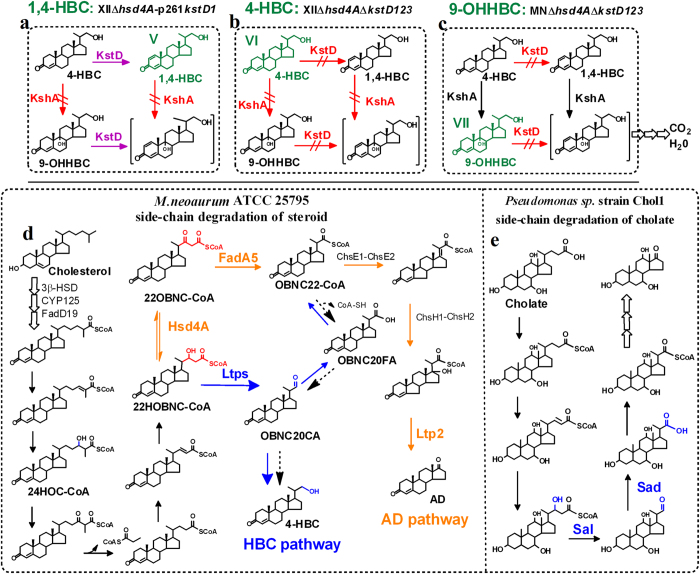
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of sterol catabolism and the combinatorial construction of HBCs producing strains.
(a) The construction of strain XIIΔhsd4A-p261kstD1. To construct XIIΔhsd4A-p261kstD1, hsd4A was deleted in a kshAs-null mutant and then kstD1 was overexpressed. The resulting strain XIIΔhsd4A-p261kstD1 transformed phytosterols to 1,4-HBC as the major product. (b) The construction of strain XIIΔhsd4AΔkstD123. To construct XIIΔhsd4AΔkstD123, hsd4A was deleted in a kshAs-null mutant and then kstD1, kstD2 and kstD3 were knocked out sequentially. The resulting strain XIIΔhsd4AΔkstD123 transformed phytosterols to 4-HBC as the major product. (c) The construction of strain MNΔhsd4AΔkstD123. To construct MNΔhsd4AΔkstD123, hsd4A was deleted in M. neoaurum ATCC 25795 and then kstD1, kstD2 and kstD3 were knocked out sequentially. The resulting strain MNΔhsd4AΔkstD123 transformed phytosterols to 9-OHHBC as the major product. 9-OHHBC, 9,22-dihydroxy-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-3-one. (d) Proposed metabolism of the sterol side chain for the production of C19 and C22 steroids in M. neoaurum ATCC 25795. The conversion from 22HOBNC-CoA to AD was designated as the AD pathway (orange arrows) and has been proposed as the sole pathway of sterol side-chain degradation. Here, a new pathway is proposed: the conversion from 22HOBNC-CoA to 4-HBC (designated as the HBC pathway, blue arrows). Between the two pathways, 22HOBNC-CoA is the branching-node, which leads to AD via the catalysis of Hsd4AMN and leads to 4-HBC via an aldolytic reaction. The β-hydroxybutyryl-CoA moiety of 22HOBNC-CoA and acetoacetyl-CoA moiety of 22OBNC-CoA are labelled in red, which were the active substrates of Hsd4AMN in vitro. 24HOC-CoA, 24-hydroxy-3-oxo-chol-4-en-26-oyl CoA; 22HOBNC-CoA, 22-hydroxy-3-oxo-25,26-bisnorchol-4-en-24-oyl CoA; 22OBNC-CoA, 3,22-dioxo-25,26-bisnorchol-4-ene-24-oyl CoA; OBNC22-CoA, 3-oxo-22,23-bisnorchol-4-ene-22-oyl-CoA; OBNC20FA, 3-oxo-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-20-formic acid; OBNC20CA, 3-oxo-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-20-carbaldehyde. (e) The proposed pathway of cholate side-chain degradation in Pseudomonas sp. strain Chol137. sal, an aldol-lyase; sad, an aldehyde dehydrogenase. Intercepted arrows (red) indicate the blockage of the target reaction by gene deletion. Arrows in purple signify the enhanced KstD1 activity. Compounds in green are the major products accumulated in constructed strains. The compound in brackets is an unstable compound that will lead to the decomposition of steroid nucleus and further degradation. Dashed arrows indicate the proposed way for HBCs formation previously suggested by Szentirmai32. Arrows in arrays signify multiple reaction steps.