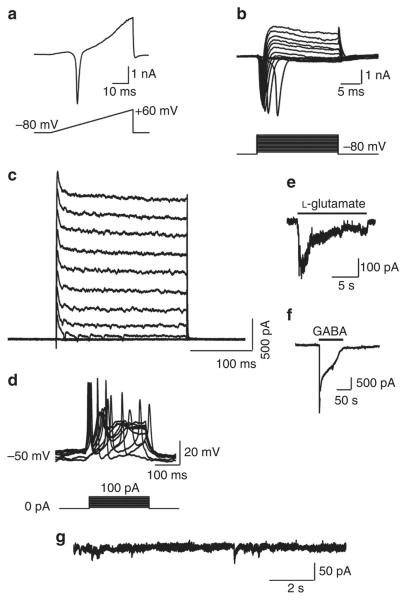
Figure 4. Electrophysiological characterization of shp19 iNs from IMR90 fibroblasts.
(a) Representative traces of membrane currents recorded with a ramp protocol (lower panel, a voltage ramp from −80 mV to +60 mV over 500 ms). Fast activating Na+ current was prominent. (b) Representative current traces (upper panel) recorded in voltage-clamp mode. Cells were depolarized by voltage steps from −80 to +60 mV in 10-mV increments (Δ10 mV, upper panel). The lower panel shows the current–voltage (I–V) relationship for sodium current. (c) Inward currents are tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-dependent sodium currents. (d) Traces of evoked action potentials in current-clamp mode. Step currents were injected from 0–100 pA in 10 pA increments. (e and f) Local application of either 15 mM l-glutamate (e), or 15 mM GABA (f) elicited current responses. (g) miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents were recorded in voltage-clamp mode from shp19 iN cells without co-culture.