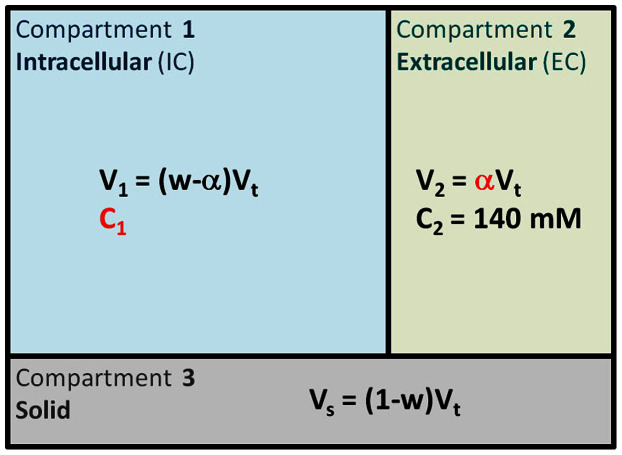
Figure 2. Three-compartment model.
In this simple model, we assume that each voxel can be separated in three compartments. Compartment 1 corresponds to the intracellular volume V1 (in L) of sodium concentration C1 (in mmol/L, or mM). Compartment 2 corresponds to the extracellular volume V2 of sodium concentration C2. These two compartments correspond to the total fluid space of the model. Compartment 3 of volume Vs corresponds to all the ‘solid’ components within the voxel (cell membranes and nuclei, proteins, and other metabolites), where sodium content is negligible. The total volume is Vt = V1 + V2 + Vs. Unknown values of interest are the intracellular sodium concentration C1 and the extracellular volume fraction α. In this model, we consider that the extracellular sodium concentration is constant and known C2 ~ 140 mM, and that the fluid (or water) volume fraction w is also known (w ~ 0.7 in WM, w ~ 0.85 in GM).