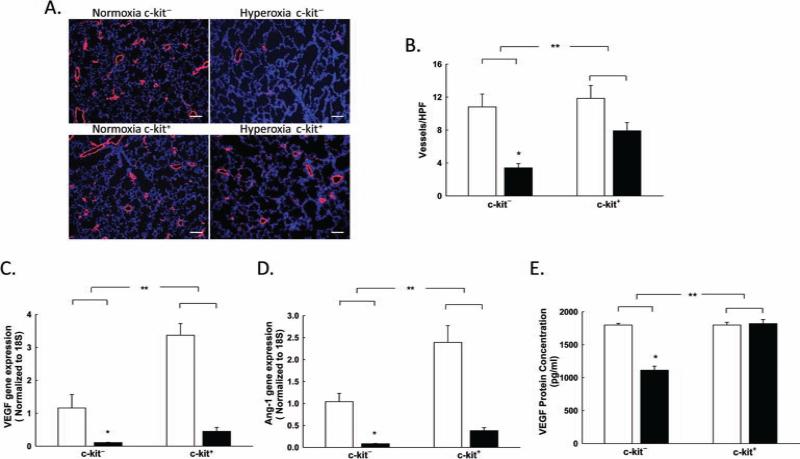
Figure 1.
BM-derived c-kit+ cells improve lung vascular density in neonatal rats with HILI. (A) Lung sections stained with vWF (red) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue) demonstrating increased vascular density/hpf in the hyperoxic pups treated with BM-derived c-kit+ cells. Original magnification: 100×. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Rarefaction of vessels in hyperoxia-exposed rats showing an increase in the number of vessels in the lungs of hyperoxic pups treated with BM-derived c-kit+ cells [*p < 0.001: normobaric normoxia (RA) c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit−, **p < 0.02: hyperoxia c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit+; n = 5–6/group]. White bars are RA, and black bars are hyperoxia. (C) Increased VEGF gene expression in hyperoxic pups treated with BM-derived c-kit+ cells (*p < 0.001: RA c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit−, **p < 0.001: hyperoxia c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit+; n=5–6/group). (D) Increased angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) gene expression in hyperoxic pups treated with BM-derived c-kit+ cells (*p < 0.001: RA c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit−, **p < 0.001: hyperoxia c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit+; n = 5–6/group). (E) Increased lung VEGF protein concentration in hyperoxic pups treated with BM-derived c-kit+ cells (*p < 0.001: RA c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit−, **p < 0.001: hyperoxia c-kit− vs. hyperoxia c-kit+; n = 5–6/group).