Figure 4.
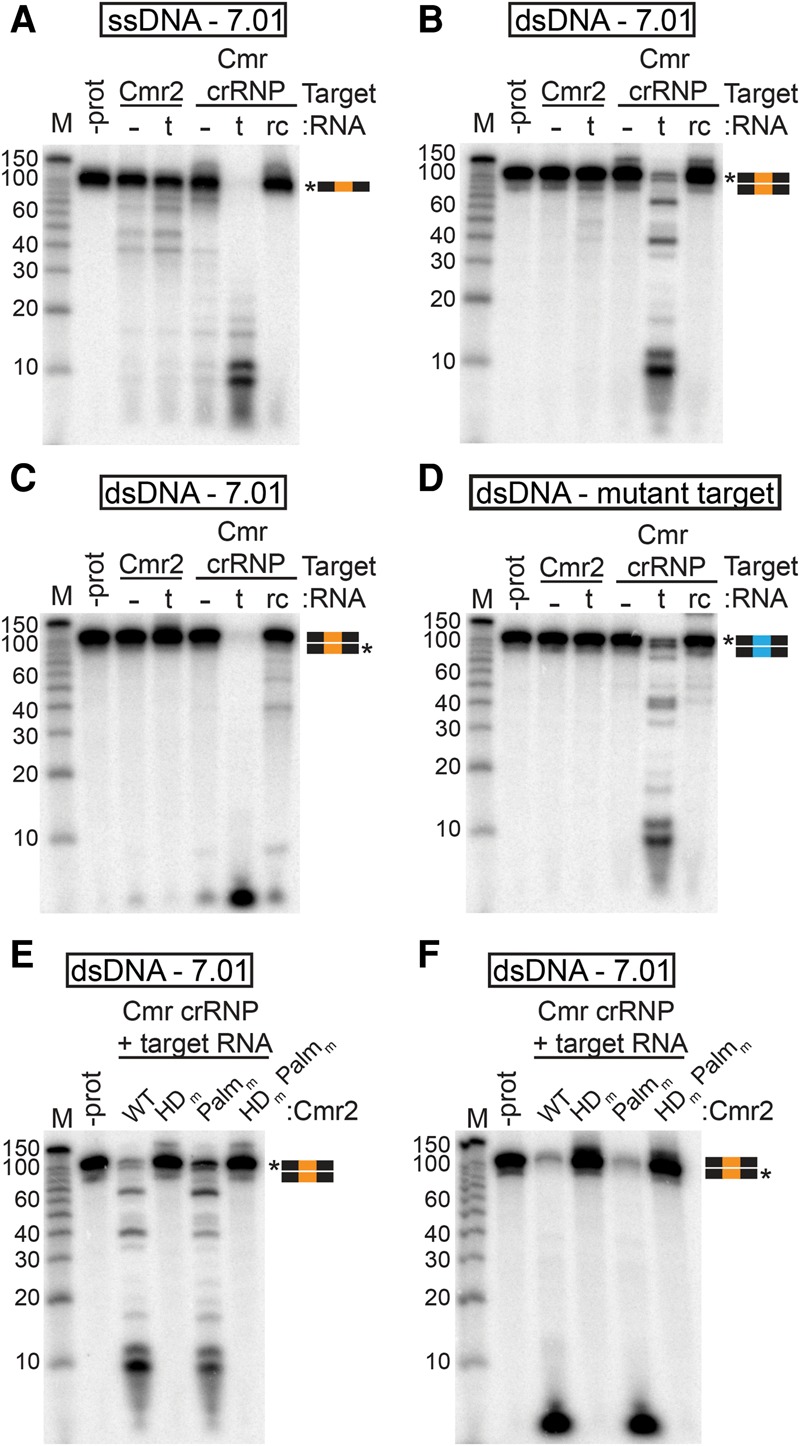
The Cmr complex cleaves dsDNA in the presence of target RNA. (A–D) Substrate analysis. Cmr2 (50 nM) and Cmr crRNP complexes (∼50 nM) were analyzed with (t) or without (−) the target RNA (complementary to the 7.01 crRNA) or with the reverse complement of the target RNA (rc). The substrates used were 5′ radiolabeled ssDNA complementary to crRNA 7.01 (A), dsDNA with a crRNA 7.01 target sequence 5′ radiolabeled on the target (B) or nontarget (C) strand, and dsDNA with a mutant 7.01 target sequence (D). (E,F) Mutant analysis. Cmr crRNP complexes containing wild-type (WT), HD domain putative active site mutant (HDm), Palm domain GGDD motif mutant (Palmm), or double-mutant (HDm,Palmm) Cmr2 were incubated with dsDNA with the crRNA 7.01 target sequence 5′ radiolabeled on the target (E) or nontarget (F) strand. Graphical representations of substrates are shown with the 7.01 target (orange) and mutant 7.01 target (blue) sequences and radiolabeled strands (asterisks) indicated. Products were analyzed by denaturing PAGE. Decade marker RNA (M) were included for size estimations.
