Figure 5.
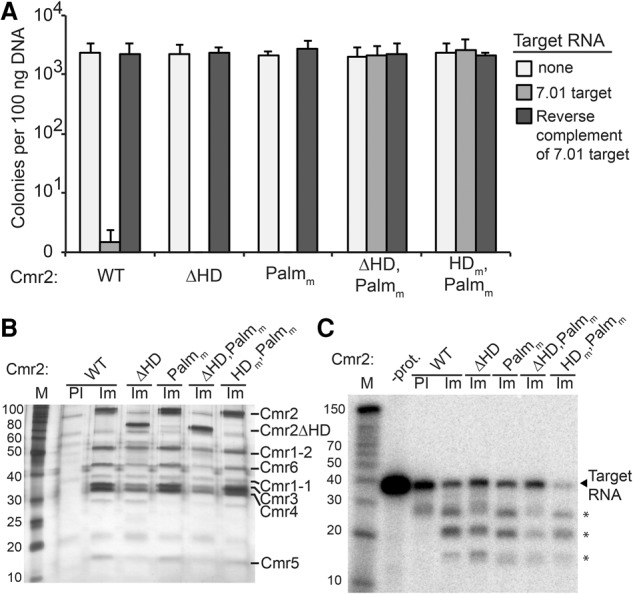
Mutation of both the HD and Palm domains of Cmr2 is required to abolish Type III-B plasmid silencing in vivo. (A) Plasmid infection of strains with Cmr2 mutants. Cmr strains expressing the indicated Cmr2 proteins (wild type [WT], ΔHD, Palmm, ΔHD,Palmm, and HDm,Palmm) were infected with plasmids expressing no target RNA (light gray), crRNA 7.01 target RNA (gray) or the reverse complement RNA (dark gray). Colony numbers are plotted with error bars indicating the standard deviation in three replicates. (B) Cmr complexes from Cmr2 mutant strains. Proteins immunoprecipitated with preimmune (PI; wild type only) or immune (Im) antibodies against Cmr2 from Cmr strains expressing the indicated Cmr2 proteins (wild type, ΔHD, Palmm, ΔHD,Palmm, and HDm,Palmm) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. Cmr protein identities are indicated based on predicted molecular weights and mass spectrometry. (C) RNA cleavage activity of Cmr complexes in Cmr2 mutant strains. Complexes immunopurified from Cmr strains expressing the indicated Cmr2 proteins (wild type, ΔHD, Palmm, ΔHD,Palmm, and HDm,Palmm) were incubated with 5′ end-labeled crRNA 7.01 target RNA. Products were analyzed by denaturing PAGE. Decade marker RNAs (M) were included for size estimations. Asterisks mark primary RNA cleavage products. Note that the top product migrates distinctly from the band in observed in preimmune sample in multiple experiments.
