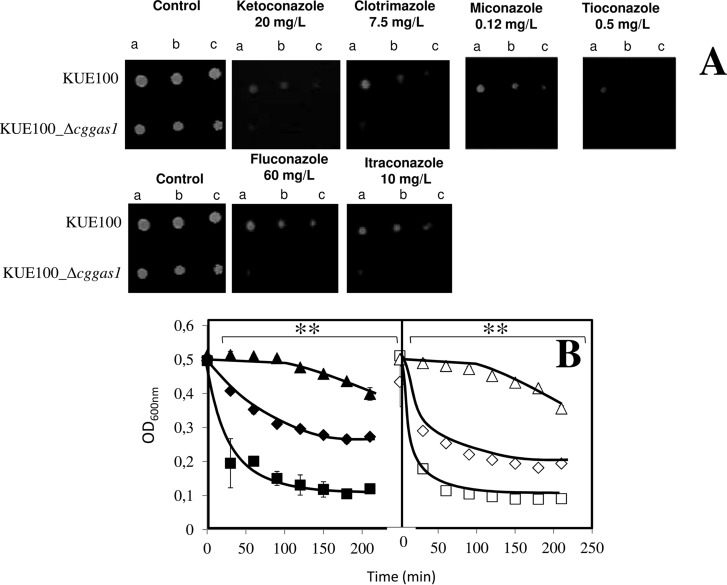
Fig. 8.
CgGas1 confers resistance to azole antifungal drugs in C. glabrata cells. (A) Comparison of the susceptibility to azole antifungal drugs, at the indicated concentrations, of the C. glabrata KUE100 wild-type and KUE100_Δcggas1 strains, in BM agar plates by spot assays. The inocula were prepared as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Cell suspensions used to prepare the spots were 1:5 (B) and 1:25 (C) dilutions of the cell suspension used in (A). The displayed images are representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) Lyticase susceptibility in Candida glabrata KUE100 (♦,■,▴) and KUE100_Δcggas1 (♢,□,▵) cells harvested in the exponential phase of growth in the absence of stress (♦, ♢) or upon 30 min of exposure to 30 mg/l clotrimazole (■,□), or in the exponential phase of growth reached upon adaptation to 30 mg/l clotrimazole (▴,▵). After addition of 10 mg/l lyticase, the decrease in the OD600 nm of the cell suspension was measured periodically and indicated as a percentage of the initial OD600 nm. The indicated values are averages of at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent the corresponding standard deviations. **p < .01.