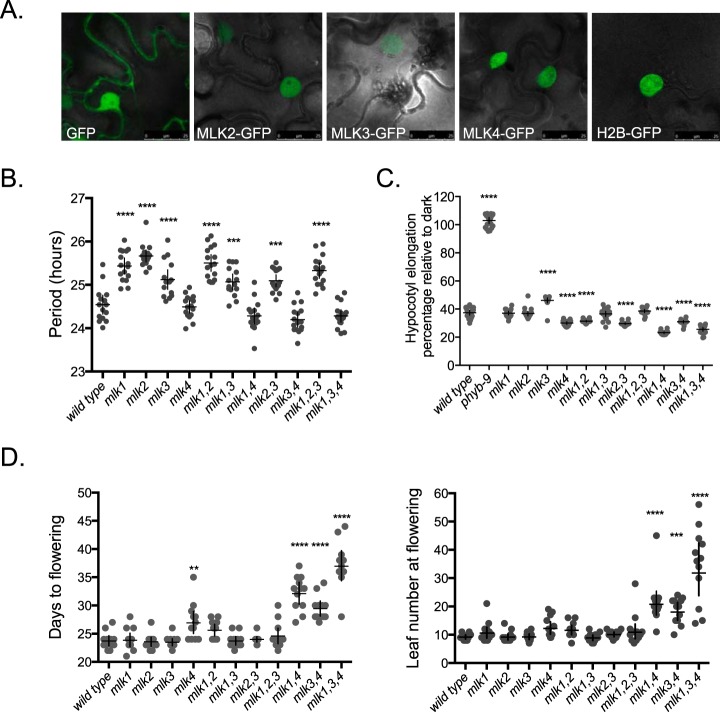
Fig. 3.
Characterization of the MUT9-LIKE KINASES. A, MLK2, MLK3, and MLK4 localize to the nucleus. Comparison of GFP, MLK2-GFP, MLK3-GFP, and MLK4-GFP to histone H2B-GFP (nuclear marker). Scale bar is 25 μm. B, Combining mutations in the MLKs alters circadian period in A. thaliana in response to 20 μmol m−2sec−1 of 660 nm red light. Circadian period of a CCA1::LUC bioluminescent reporter in single, double and triple mlk mutants. n = 16, line represents mean period, error is 95% confidence interval. Significance analysis is relative to wild type. Measurements were repeated twice with similar results. C, MLKs regulate hypocotyl elongation in response to red light. Hypocotyls of 4 day-old seedlings grown under 25 μmol/m2/s 660 nm constant red light were normalized to dark controls for each genotype. n = 20. Error is 95% confidence interval. Significance analysis is relative to wild type. Measurements were repeated twice in independent biological experiments with similar results. D, MLK4 regulates time to flowering. Left graph depicts time to a 1 cm inflorescence for individual plants grown in 16 h days, 8 h nights. Right graph depicts number of leaves when 1 cm inflorescence appears in individual plants grown in 16 h days, 8 h nights. n = 12, bar is mean and error is 95% confidence interval. Significance analysis is relative to wild type. Measurements were repeated three times in independent biological experiments with similar results. For all graphs, * ≤ 0.05, ** ≤ 0.01, *** 0.001, **** ≤ 0.0001.