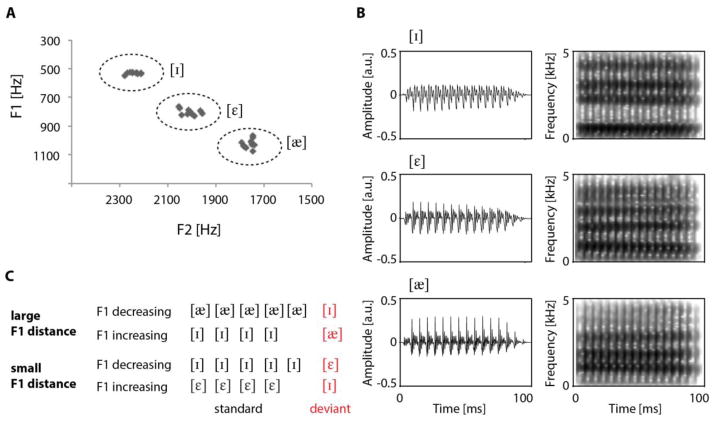
Figure 1.
A. Acoustic properties (first and second formant frequencies; F1/F2) of the vowels as obtained from a linear predictive coding (LPC) analysis. B. Waveform and spectrogram for a representative member of each vowel type. C. Illustration of passive oddball paradigm. In the large F1 distance condition, low [æ] and high [ɪ] were presented in standard position and thus set up a predictive context, violated by the respective deviants [ɪ] and [æ]. In the small F1 distance condition, high [ɪ] as standard set up a predictive context while [ε] created a relatively non-predictive context.