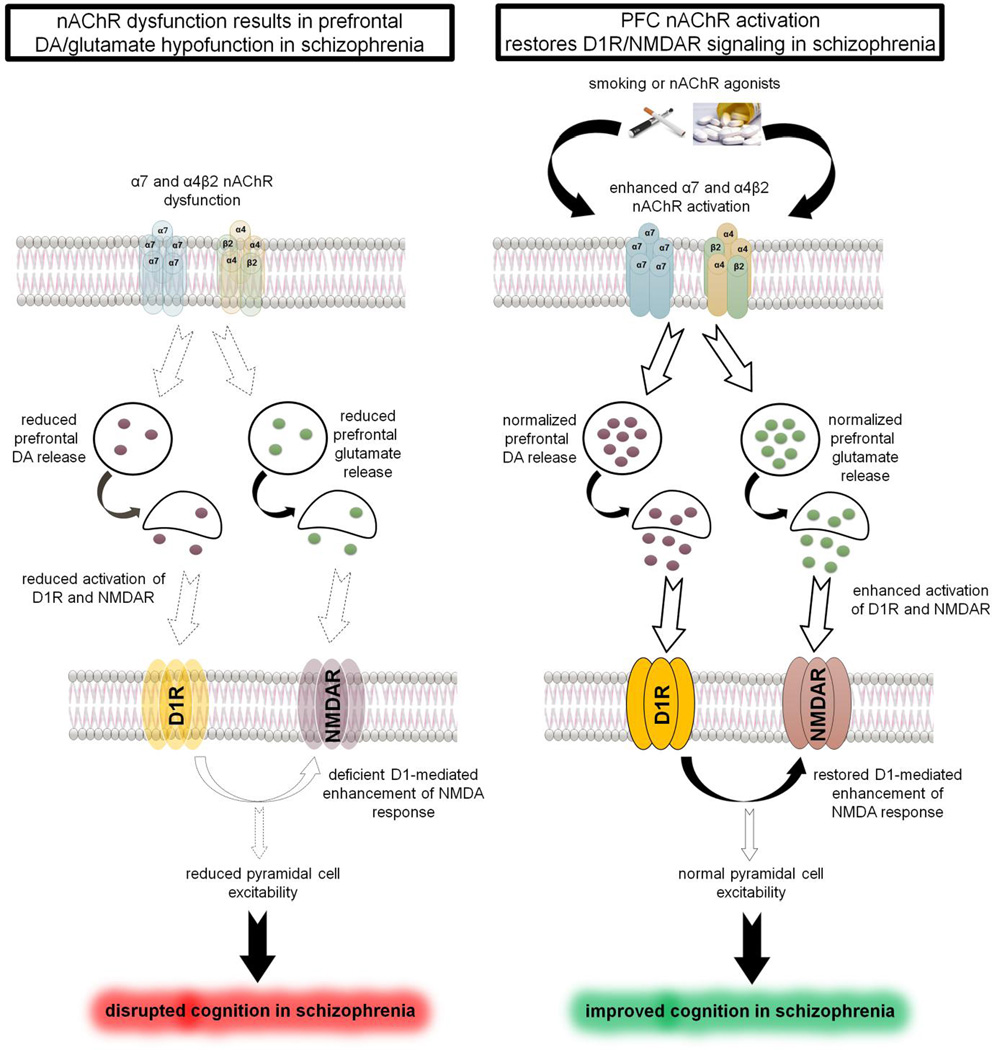
Figure 1.
Cartoon depicting the role of prefrontal nAChRs in cognitive deficits of schizophrenia. Left Panel: nAChR dysfunction in schizophrenia produces deficient DA and glutamate release in the PFC resulting in diminished D1 and NMDA receptor signaling. Reduced synergy between D1 and NMDA receptor disrupts PFC excitability and cognitive functions. Right Panel: Smoking (nicotine) or activation α4β2 and/or α7 nAChRs increases DA/glutamate release in the PFC and restore synergistic interactions between the DA and glutamate signaling to normalize PFC function and improve cognition in schizophrenia.