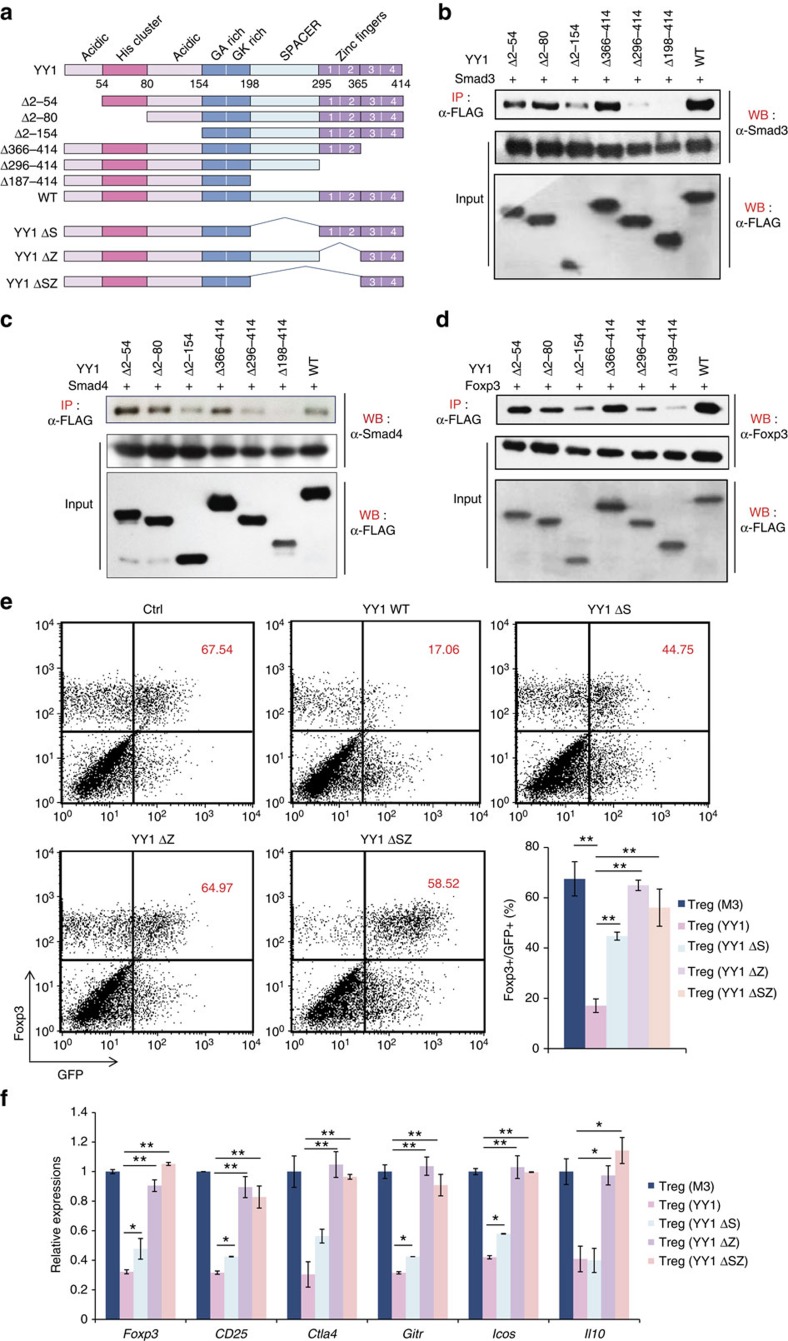
Figure 9. Spacer and zinc finger 1-2 domains of YY1 are essential for inhibition of Treg differentiation.
(a) Schematic diagram of YY1 domains. (b–d) HEK293T cells were transfected with Smad3-, Smad4- or Foxp3-expression vector together with various FLAG-tagged, YY1 domain mutant expression vectors. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG. Then, proteins were immunoblotted by an anti-Smad3 (b), anti-Smad4 (c), anti-Foxp3 (d) or anti-FLAG antibody, as indicated. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, immunoblot. (e) Naïve CD4 T cells were transduced with a retroviral vector containing control, YY1 (full length), YY1 ΔS, YY1 ΔZ or YY1 ΔSZ, and differentiated into Treg cells for 4 days. Expression of Foxp3 was measured by flow cytometry. Numbers in the plots indicate percentage of Foxp3+ cells from GFP+ cells. (f) GFP+ cells from e were sorted, and total RNA was isolated. Relative amounts of the Foxp3 and Treg signature genes were measured by qRT–PCR. Experiments were performed three times with similar results. Error bars shown in b and f represent s.d. Statistical differences in e and f were analysed by Student's t-test (n=3). *P<0.05. **P<0.01.