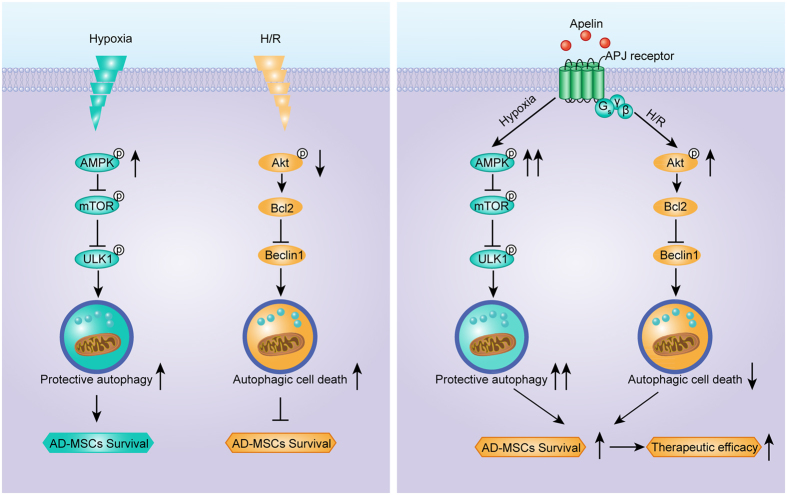
Figure 8. Schematic diagrams depicting apelin regulation of AD-MSCs autophagy under hypoxia and H/R.
Hypoxia stimulates AMPK activation and mTOR inhibition in MSCs, leading to a mild elevation of protective autophagy, and promoted MSCs survival in an autophagic aspect (the direct and overall effect of hypoxia is detrimental for MSCs survival), while apelin enhanced AMPK activation, mTOR inhibition, subsequent protective autophagy and AD-MSCs survival in hypoxia phase. On the other hand, H/R leads to a decreased activation of Akt and Bcl2 in MSCs, increasing the level of autophagic cell death, and impairs MSCs survival, while apelin enhanced activation of Akt and Bcl2 in MSCs, leading to suppression of autophagic cell death in H/R. Apelin exhibited the potential to enhance survival of engrafted MSCs via regulation of MSCs autophagy. Thus, apelin may be a potential target for optimizing MSC therapy for PAD.